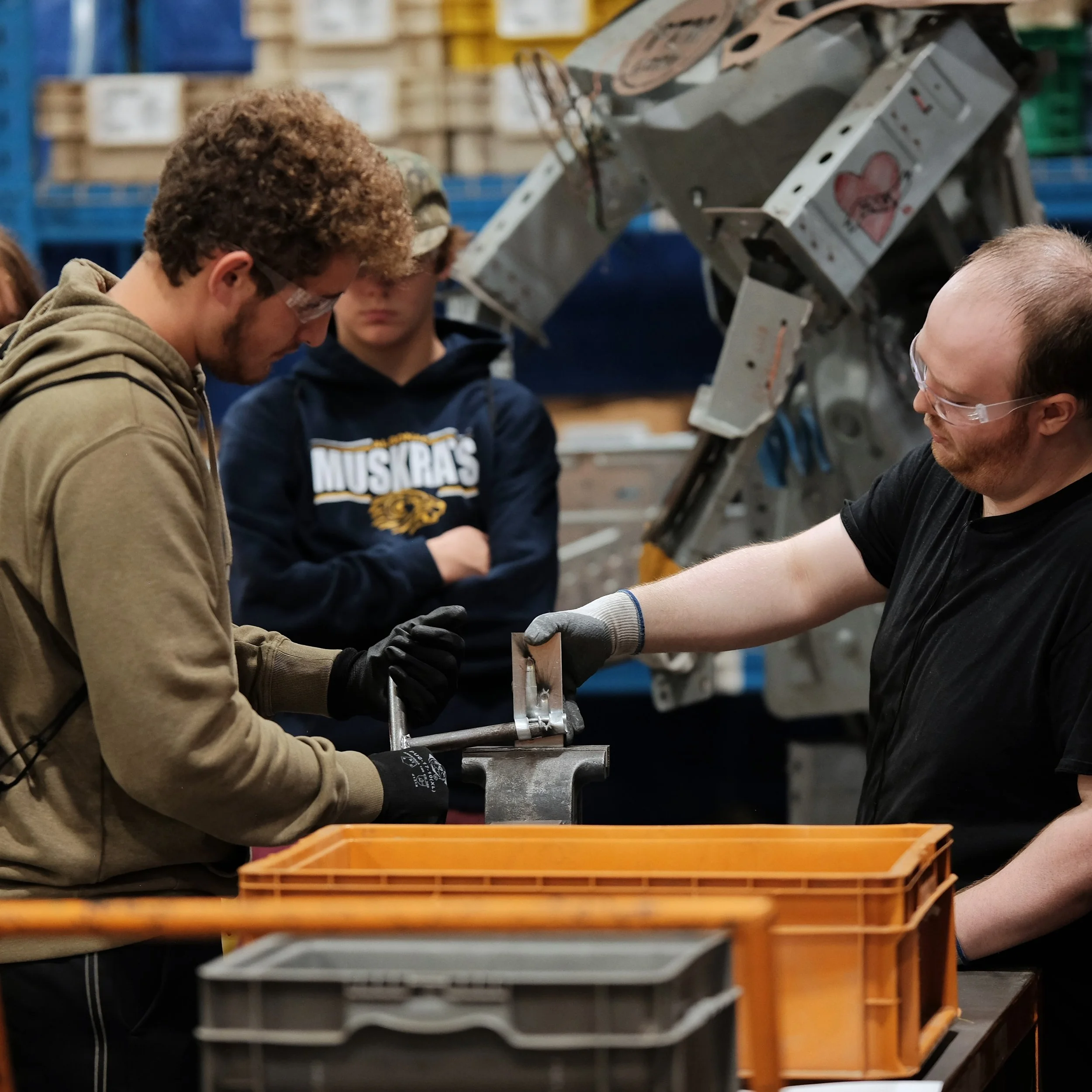
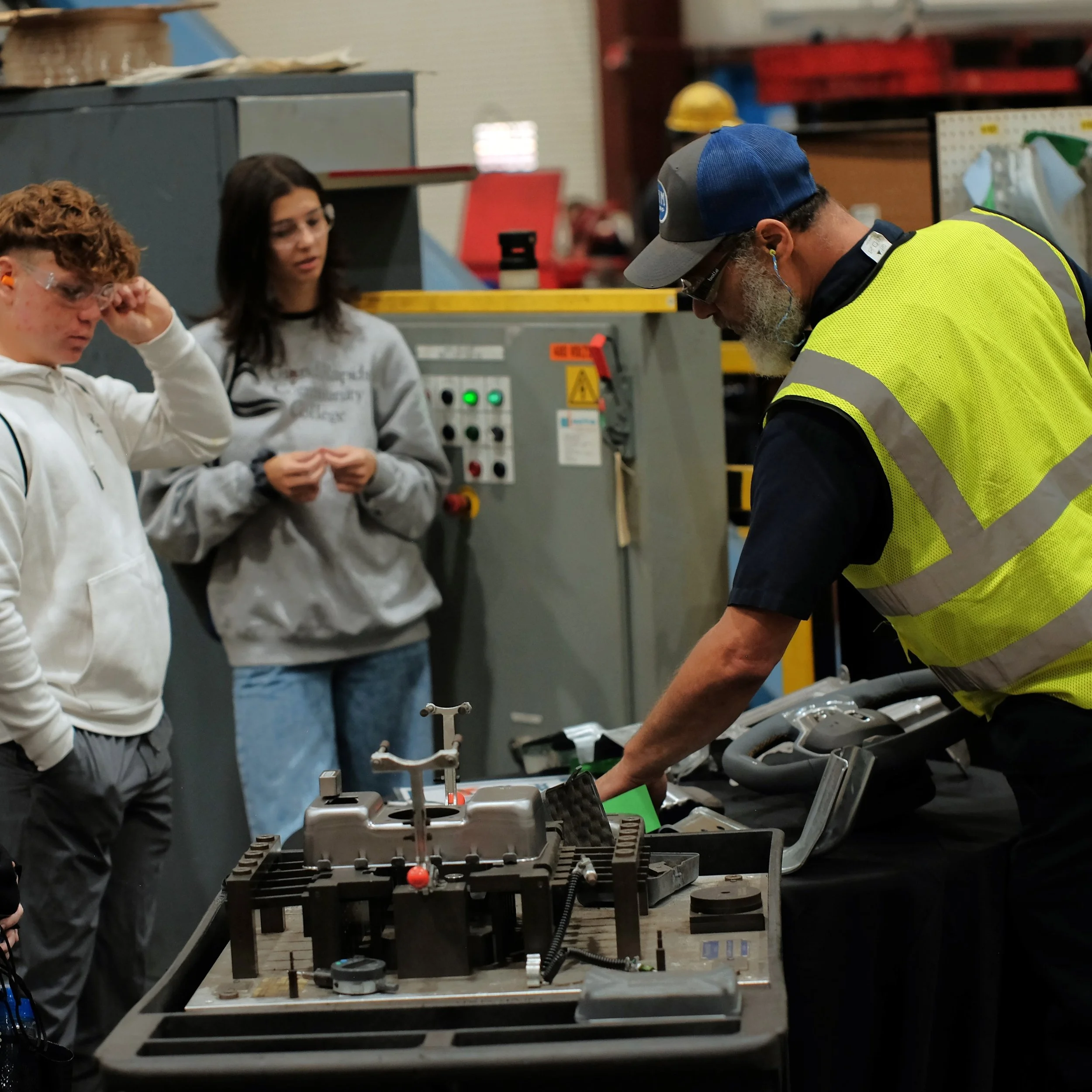
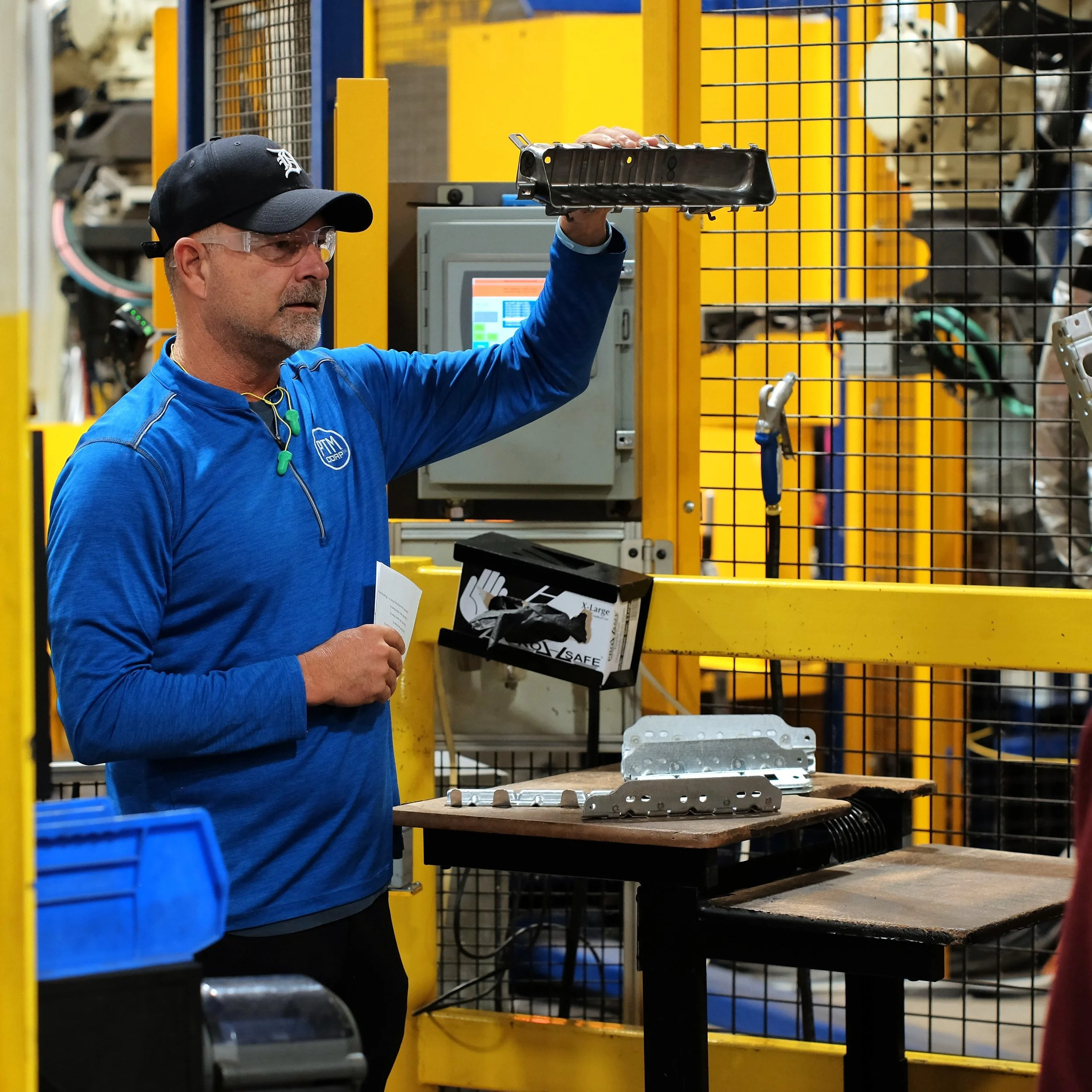
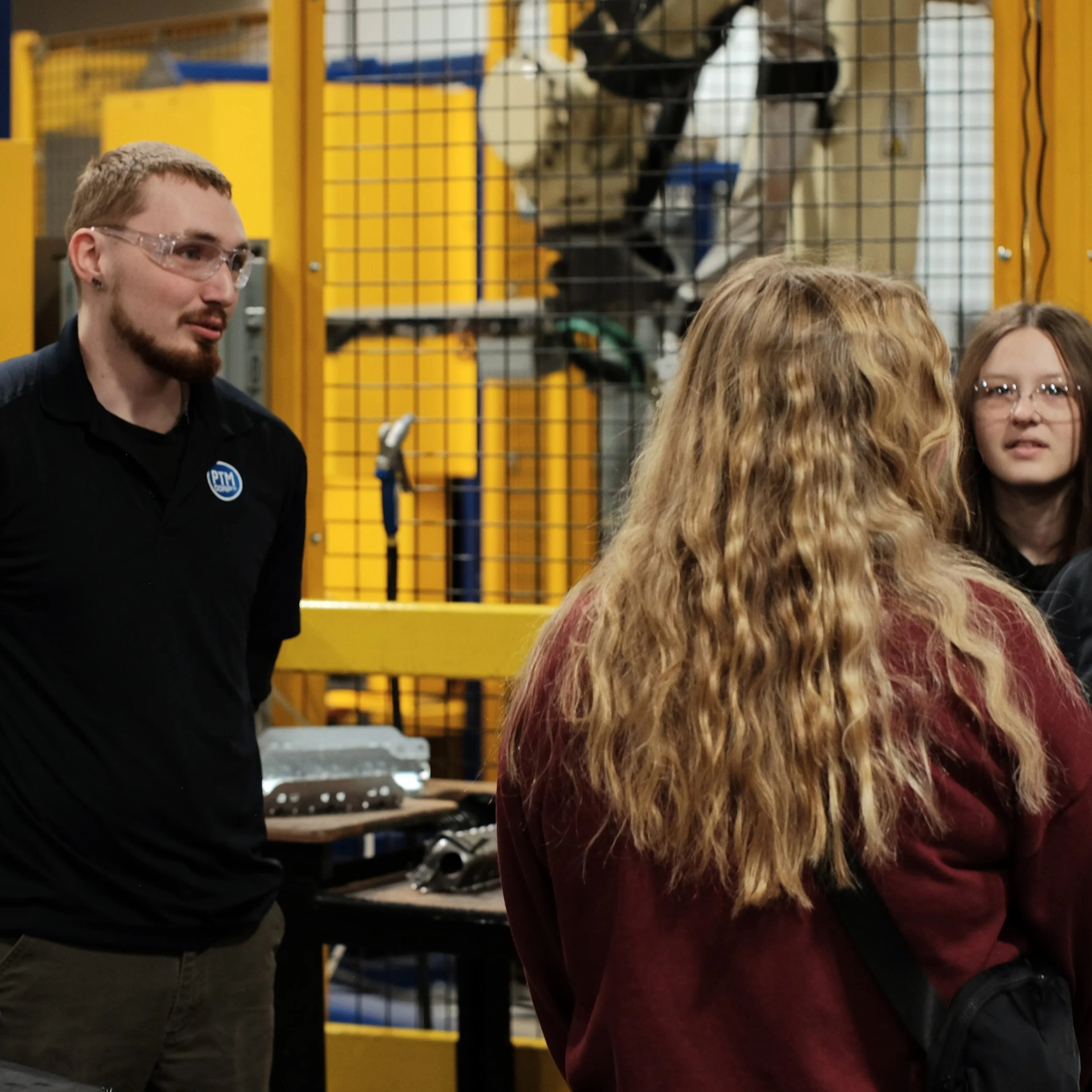
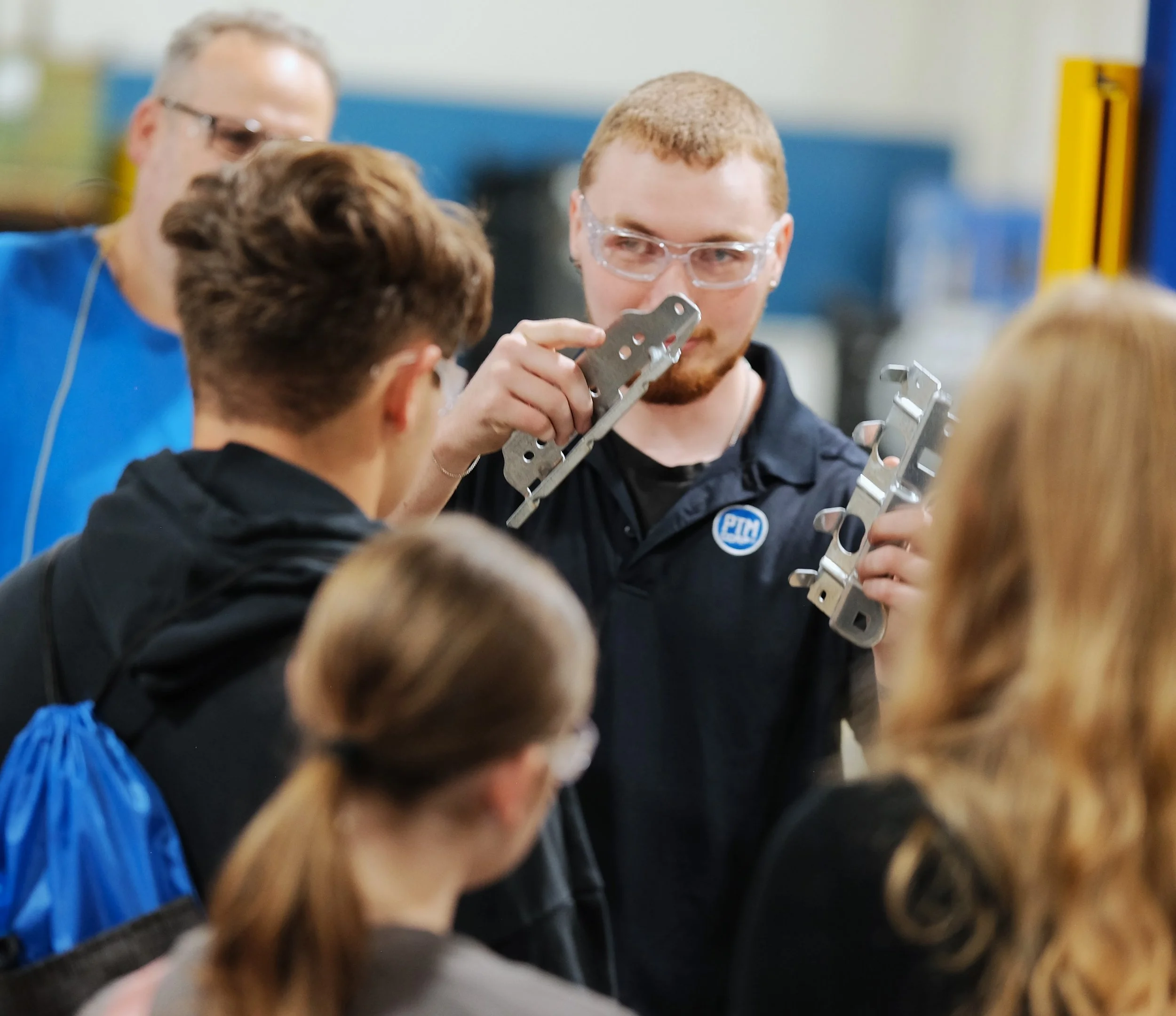
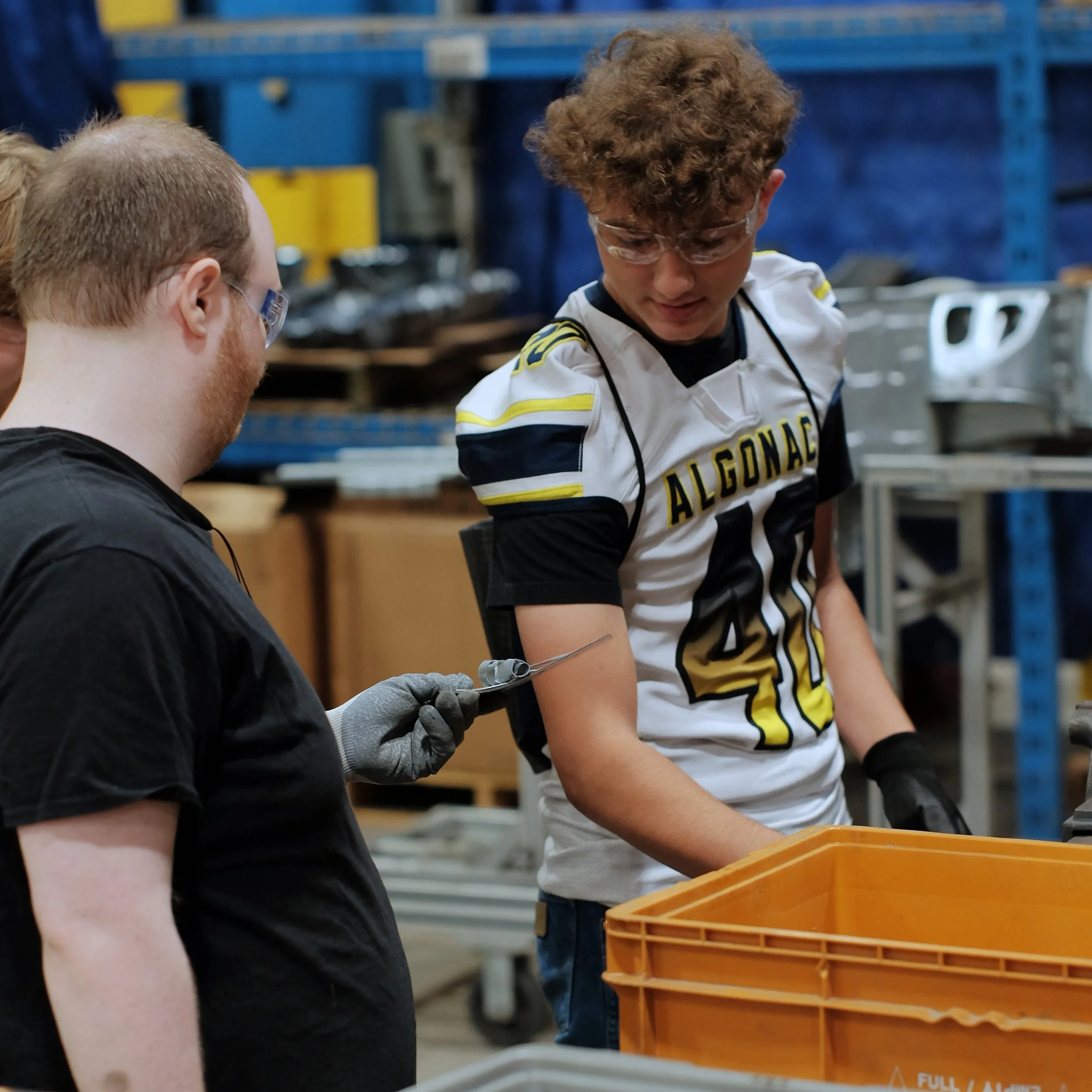
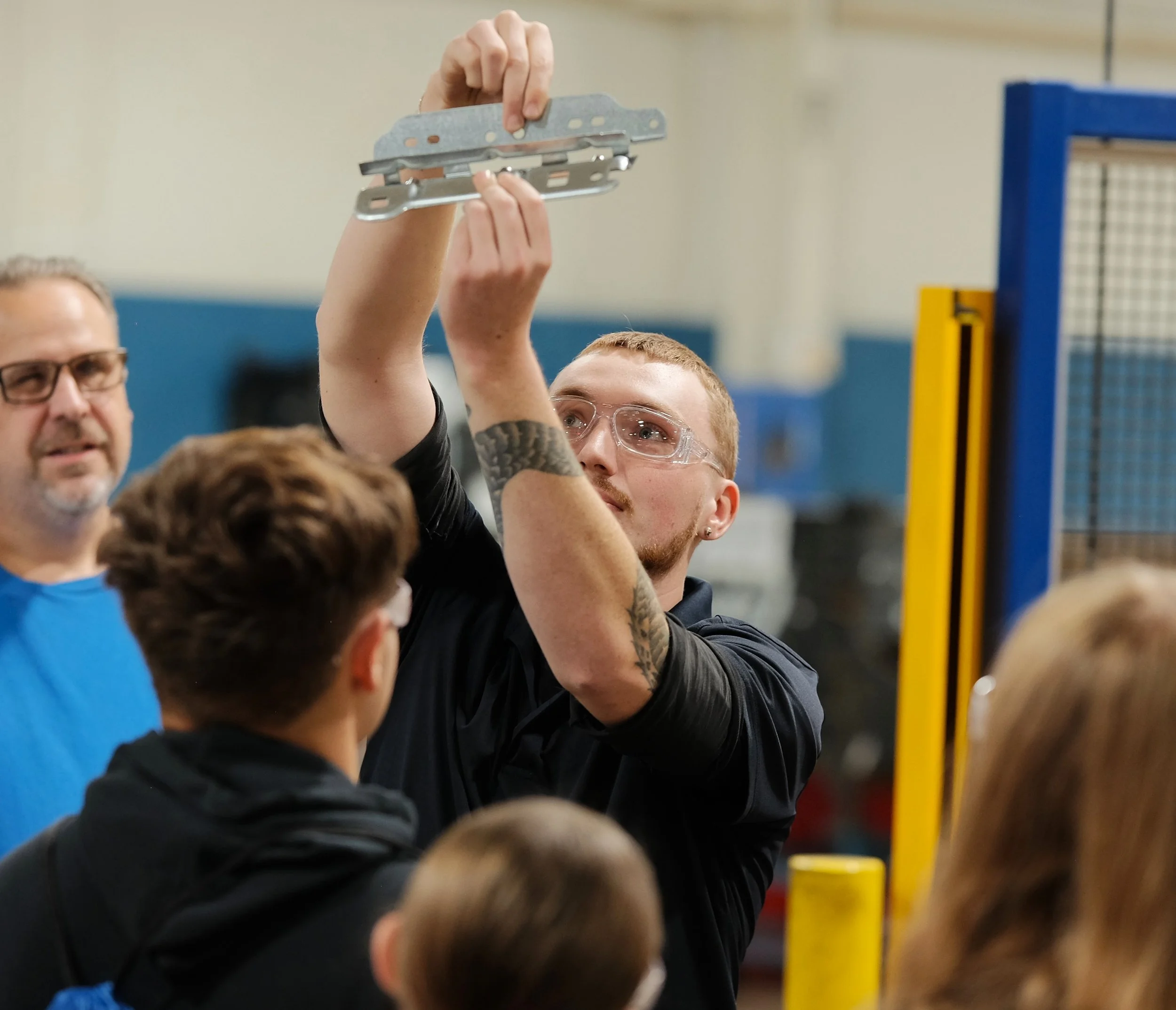
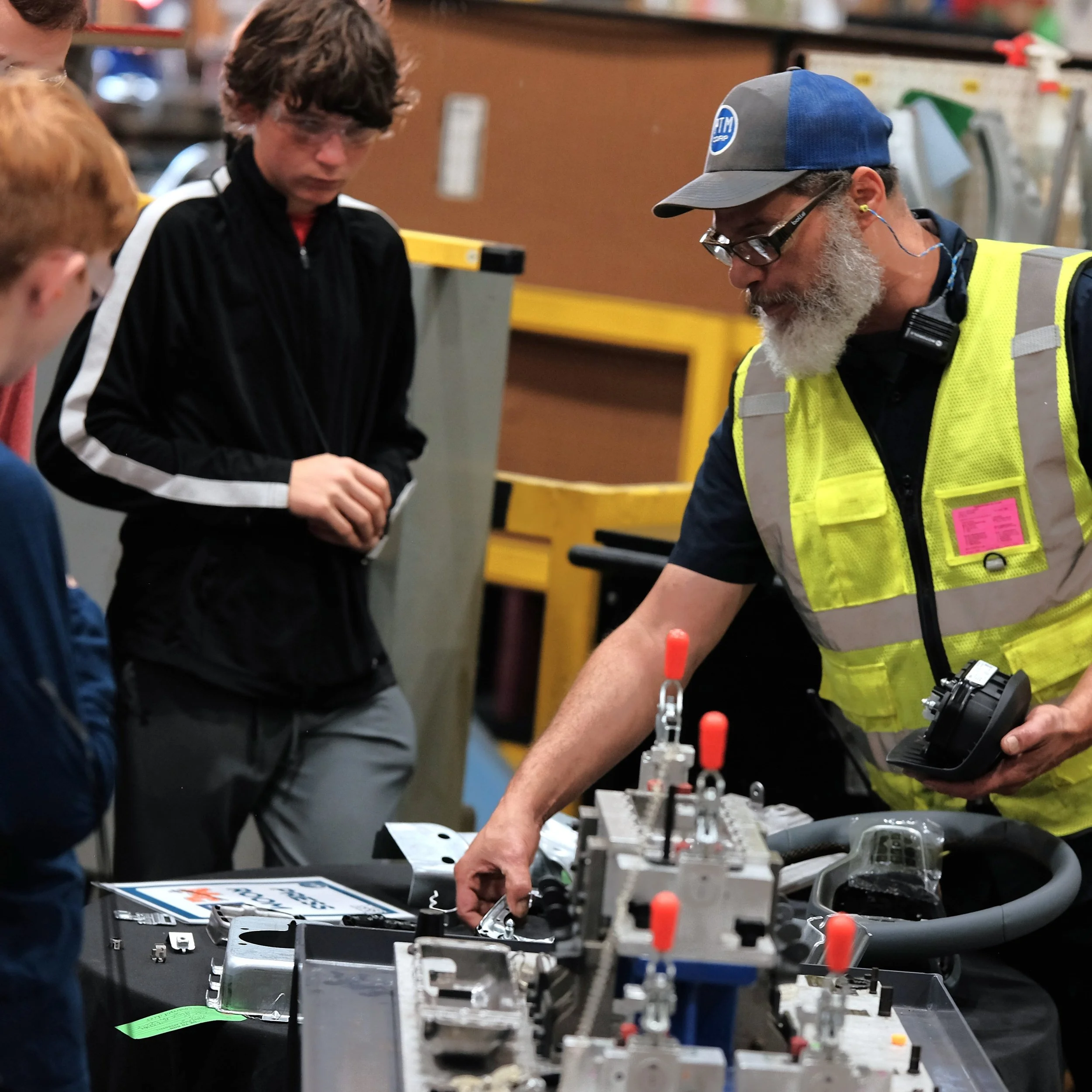
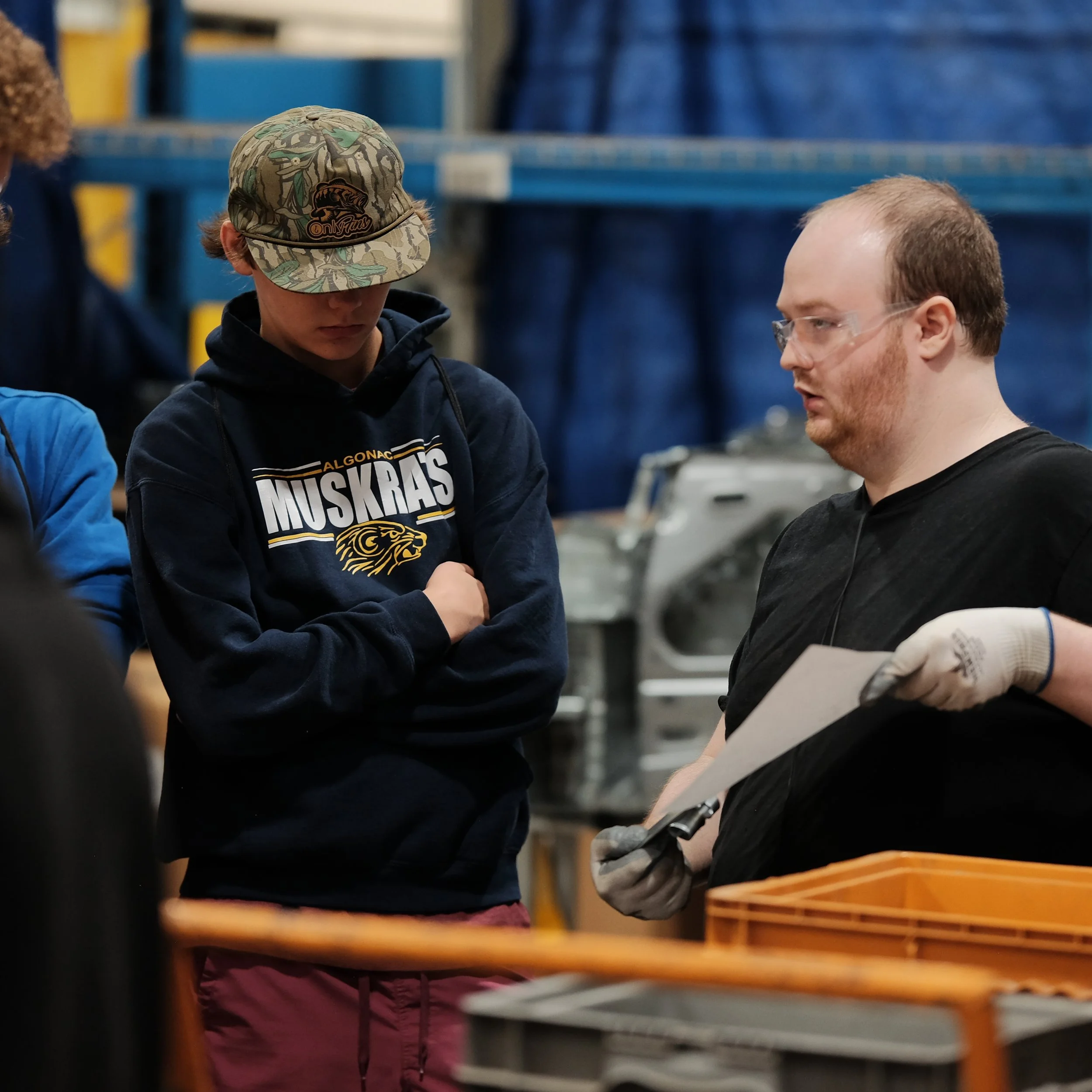Manufacturing Day 2024 Photo Gallery
Manufacturing Day 2024 Photo Gallery
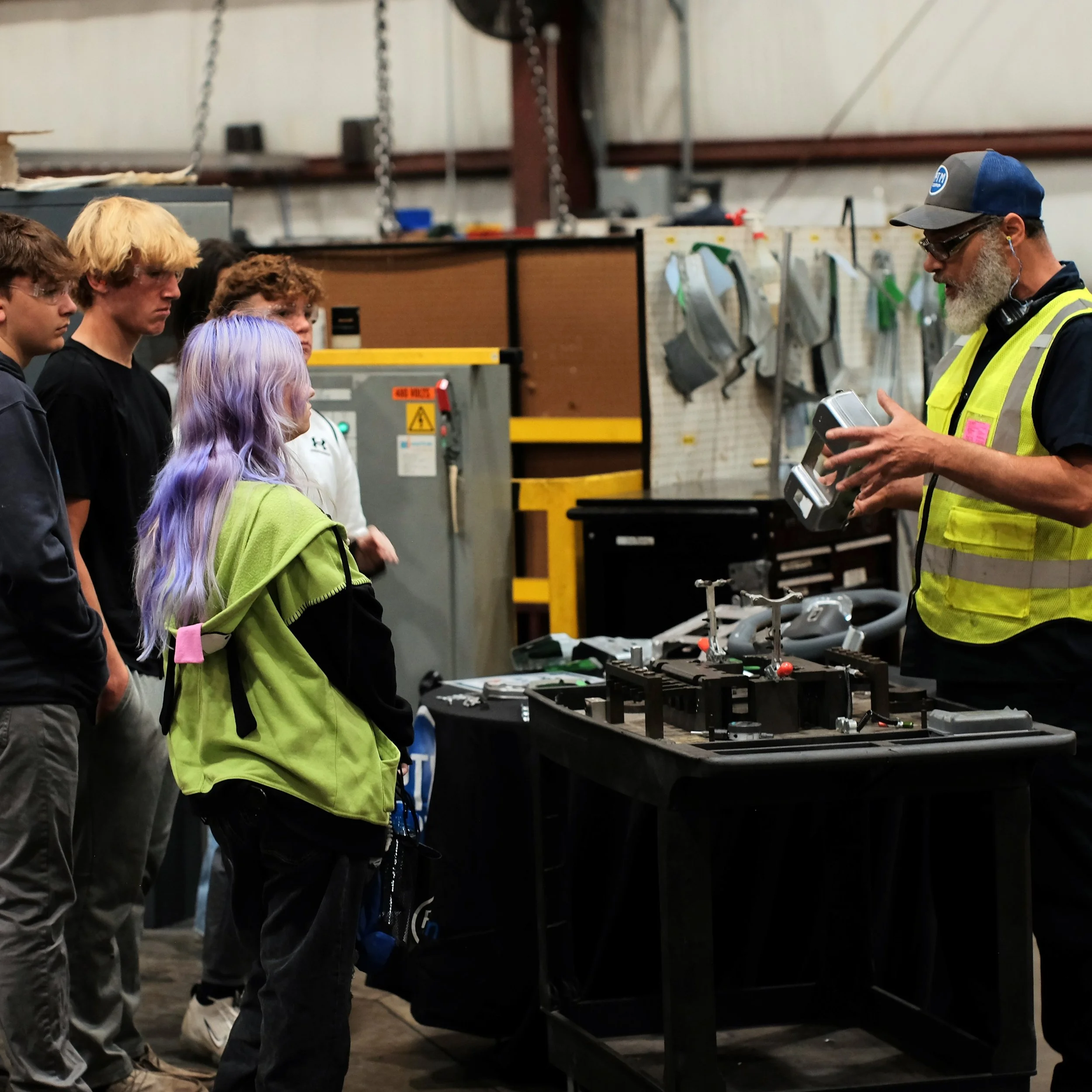
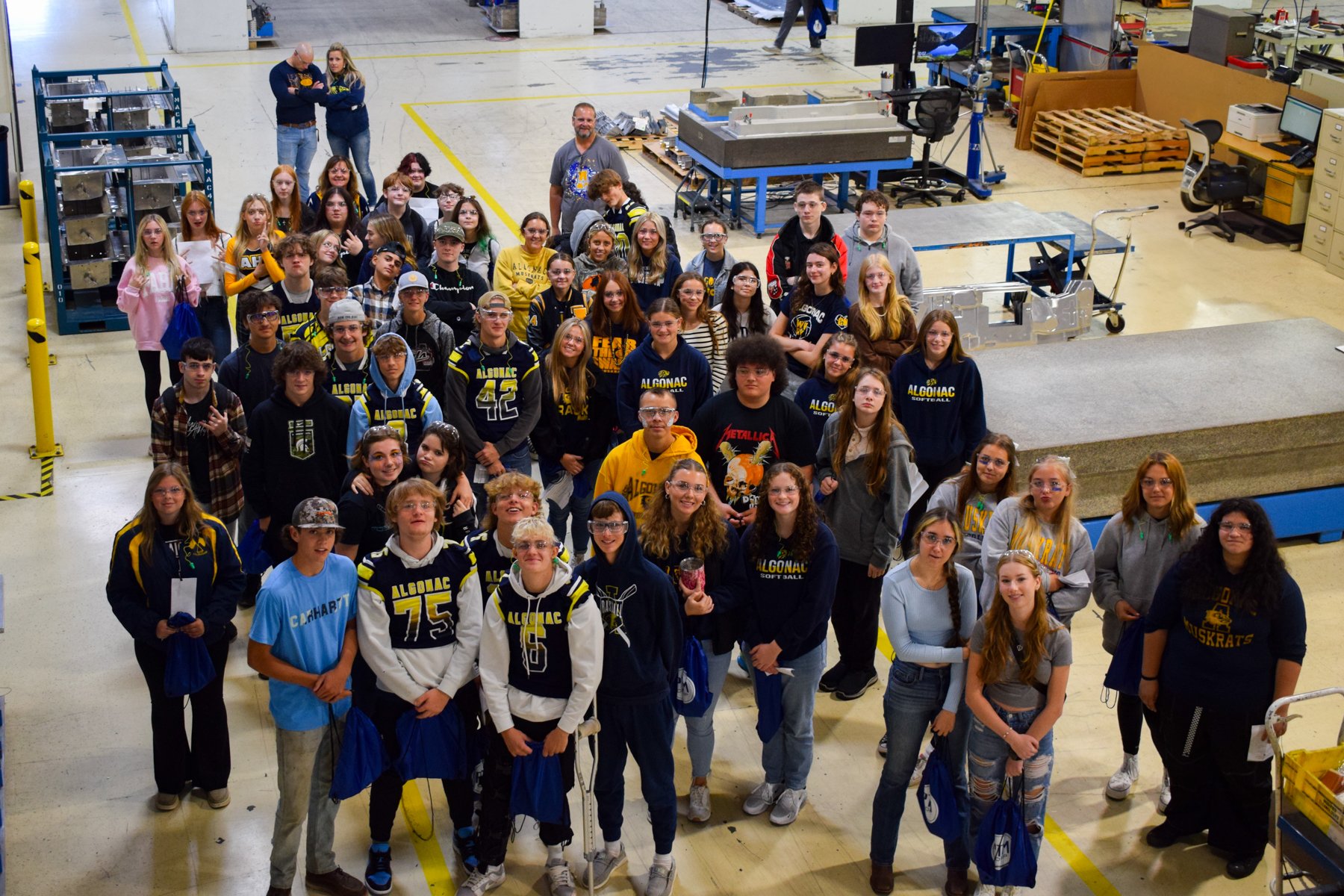
Each year, high school students tour the PTM campus to explore welding, prototyping, tool design, CNC, and many other stages of the production process. This year, we welcomed nearly 150 students from Algonac and Marine City High Schools. Our annual Manufacturing Day was a tremendous success! We’re always thrilled to inspire the next generation of manufacturers and show them how we "Make Magic with Metal." Thank you to everyone who contributed to making this day possible!
2023 Manufacturing Day Photo Gallery
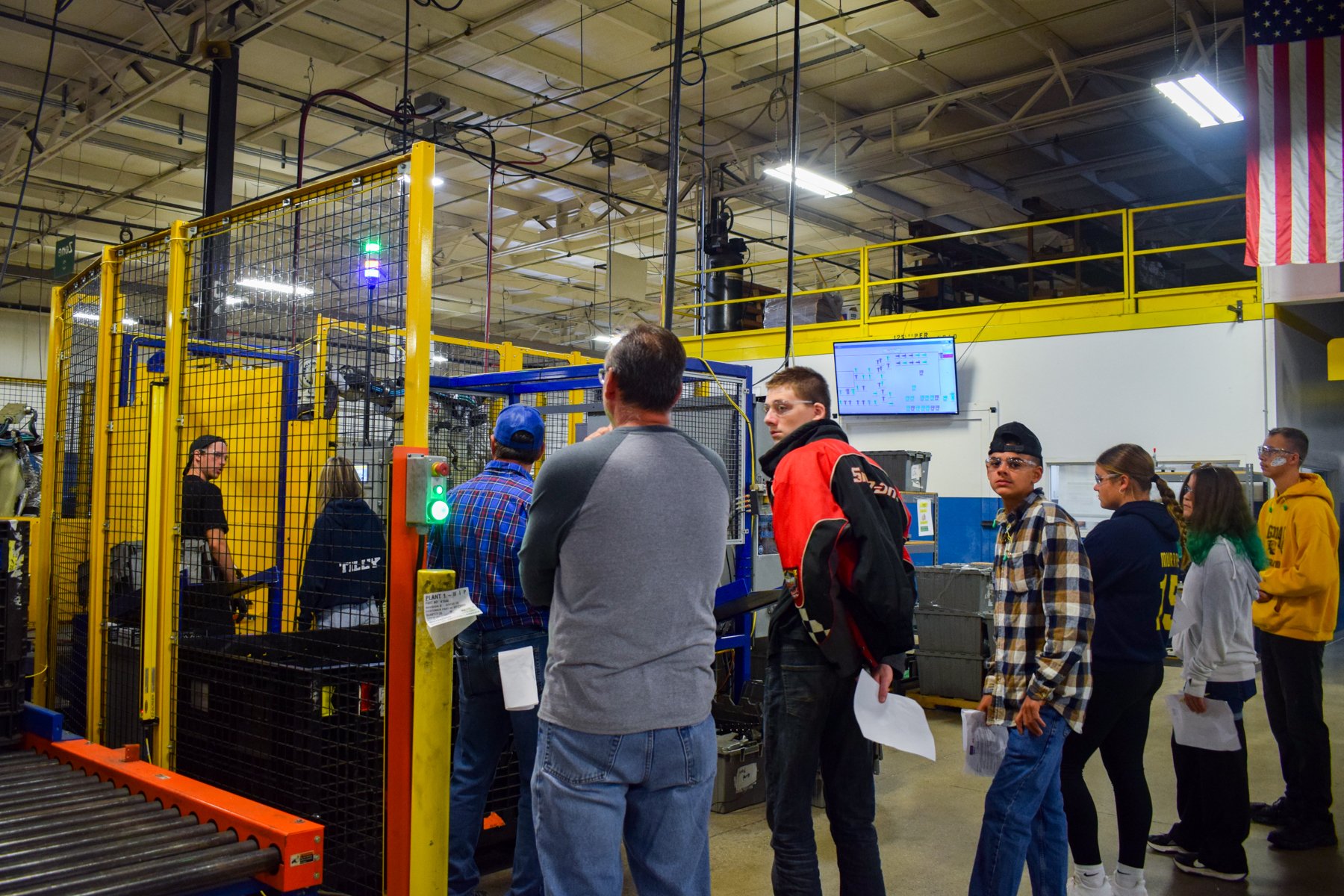
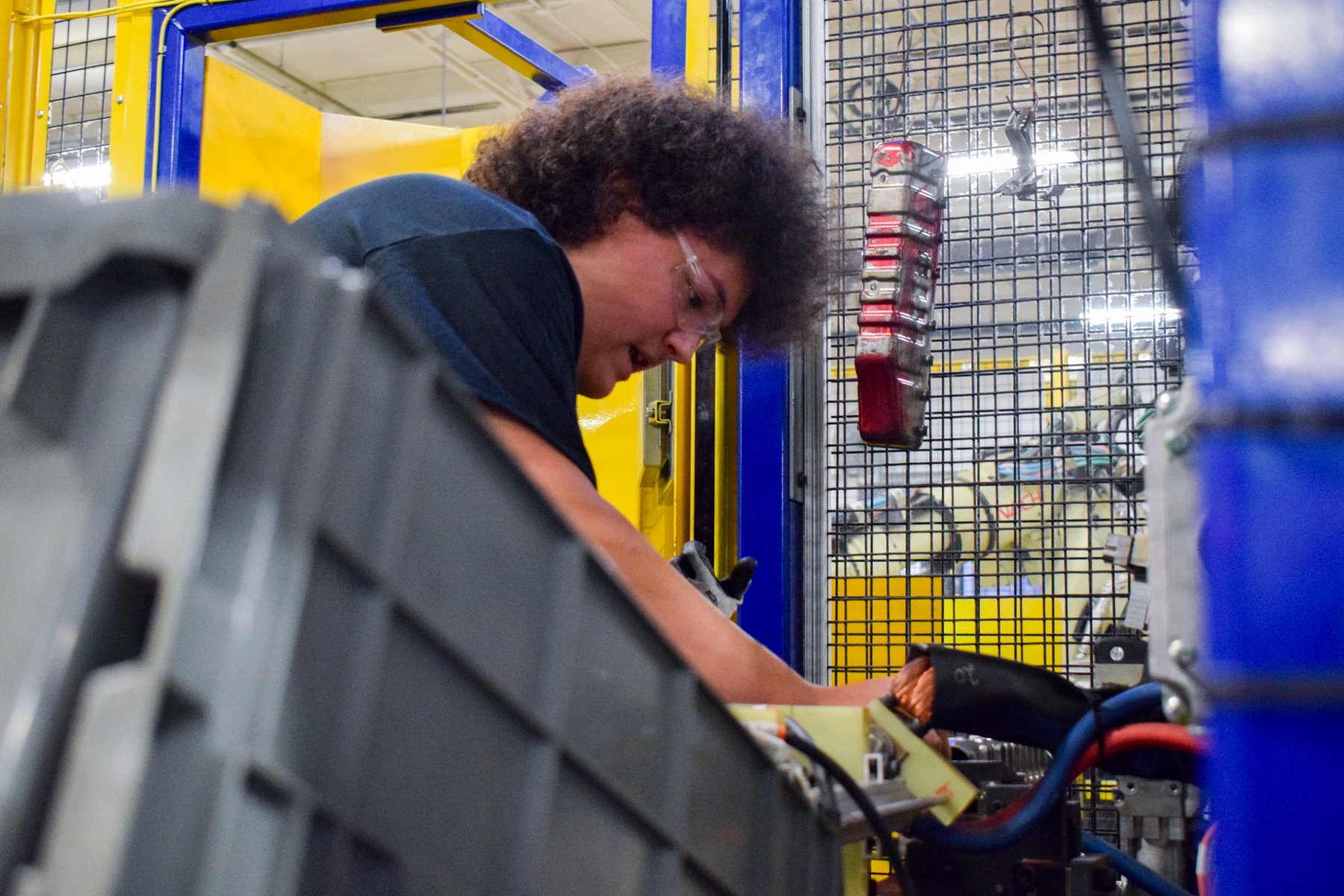
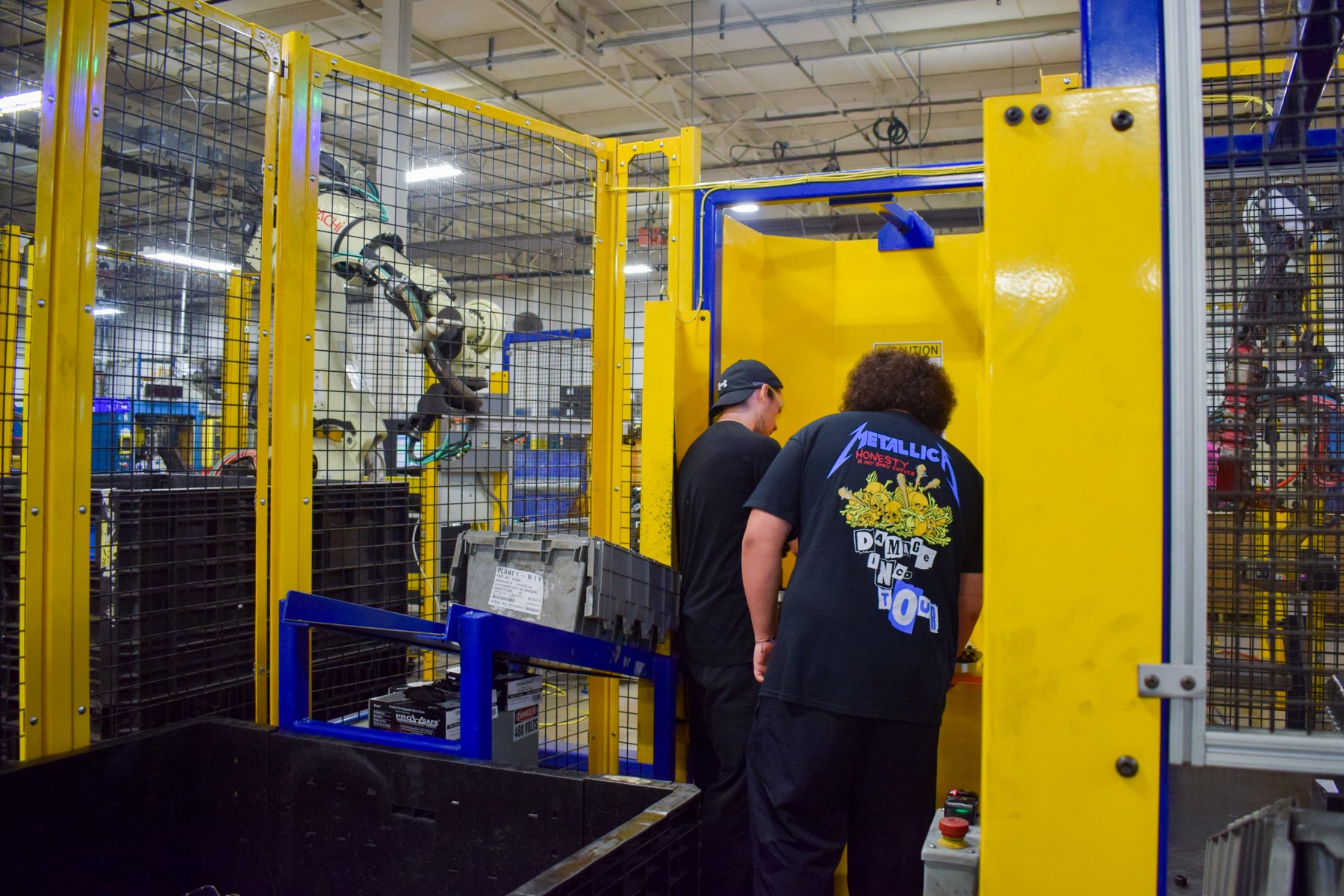
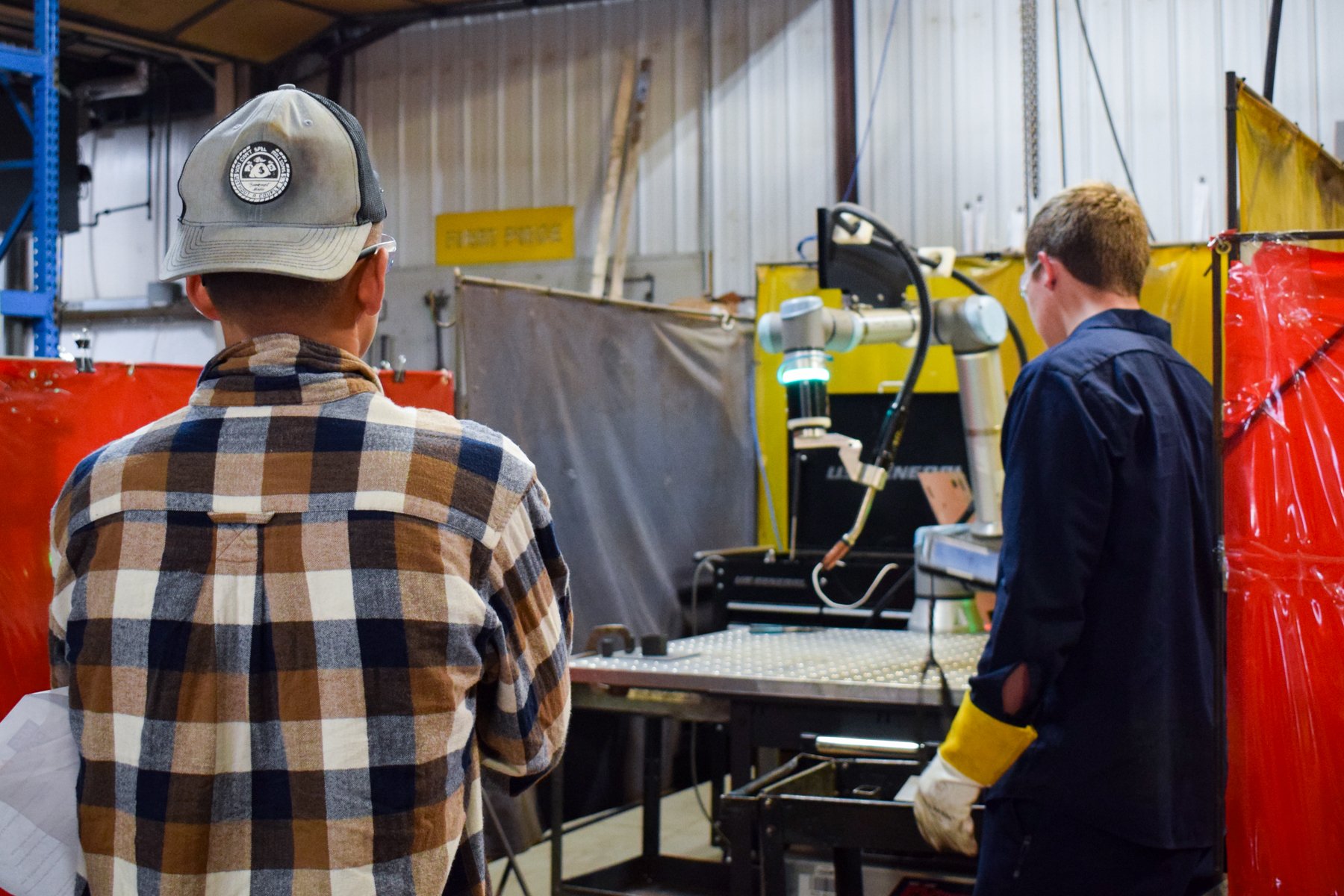
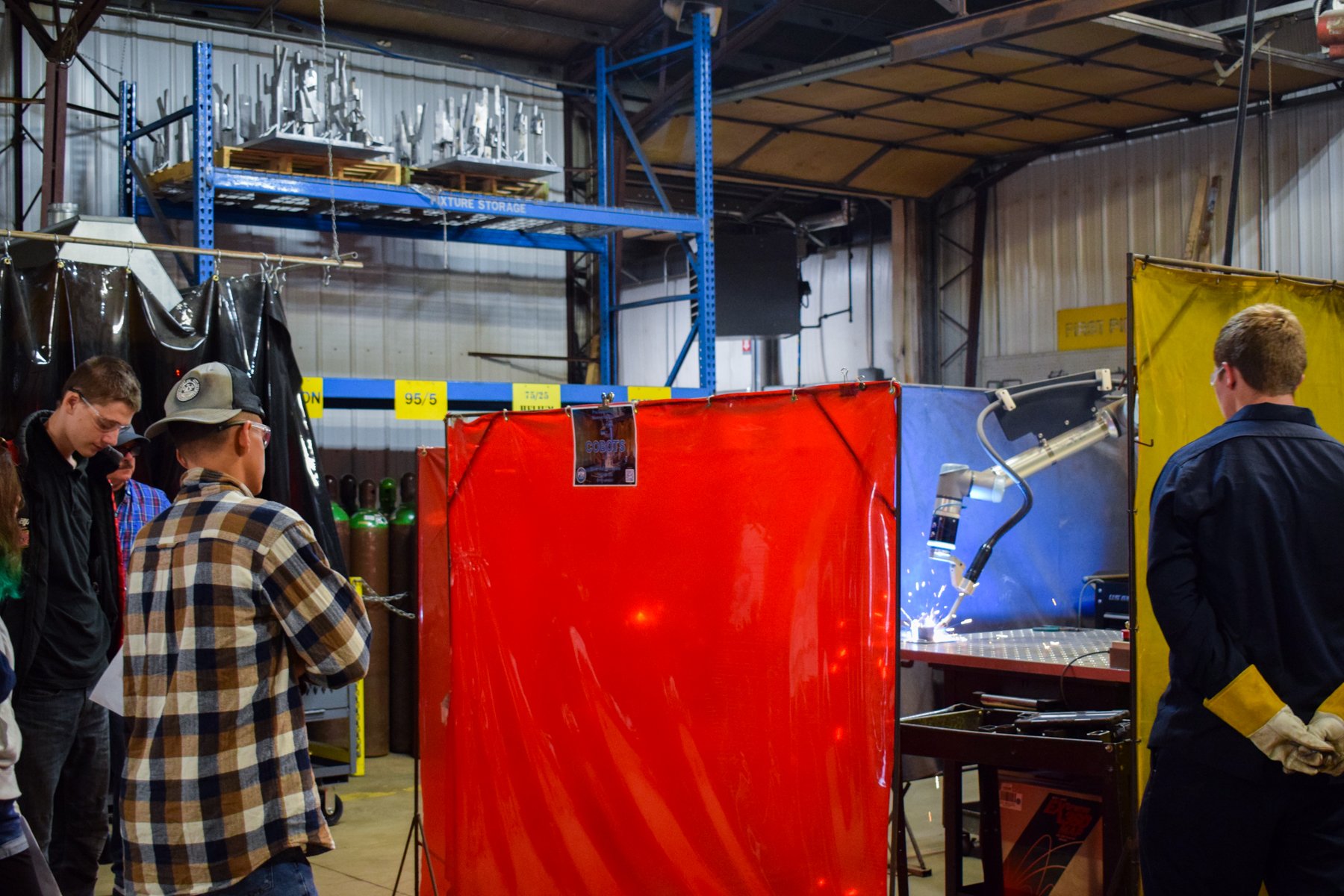
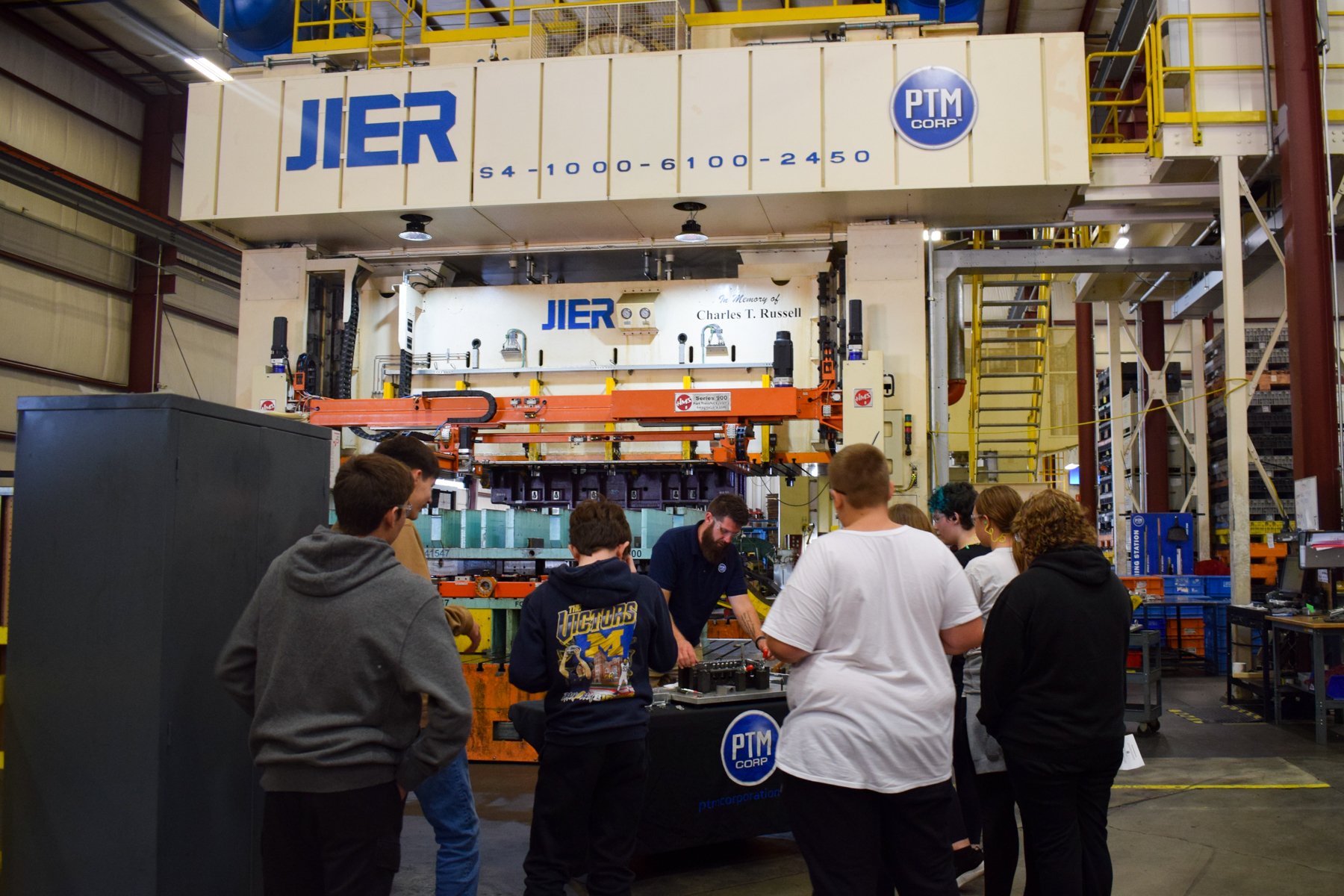
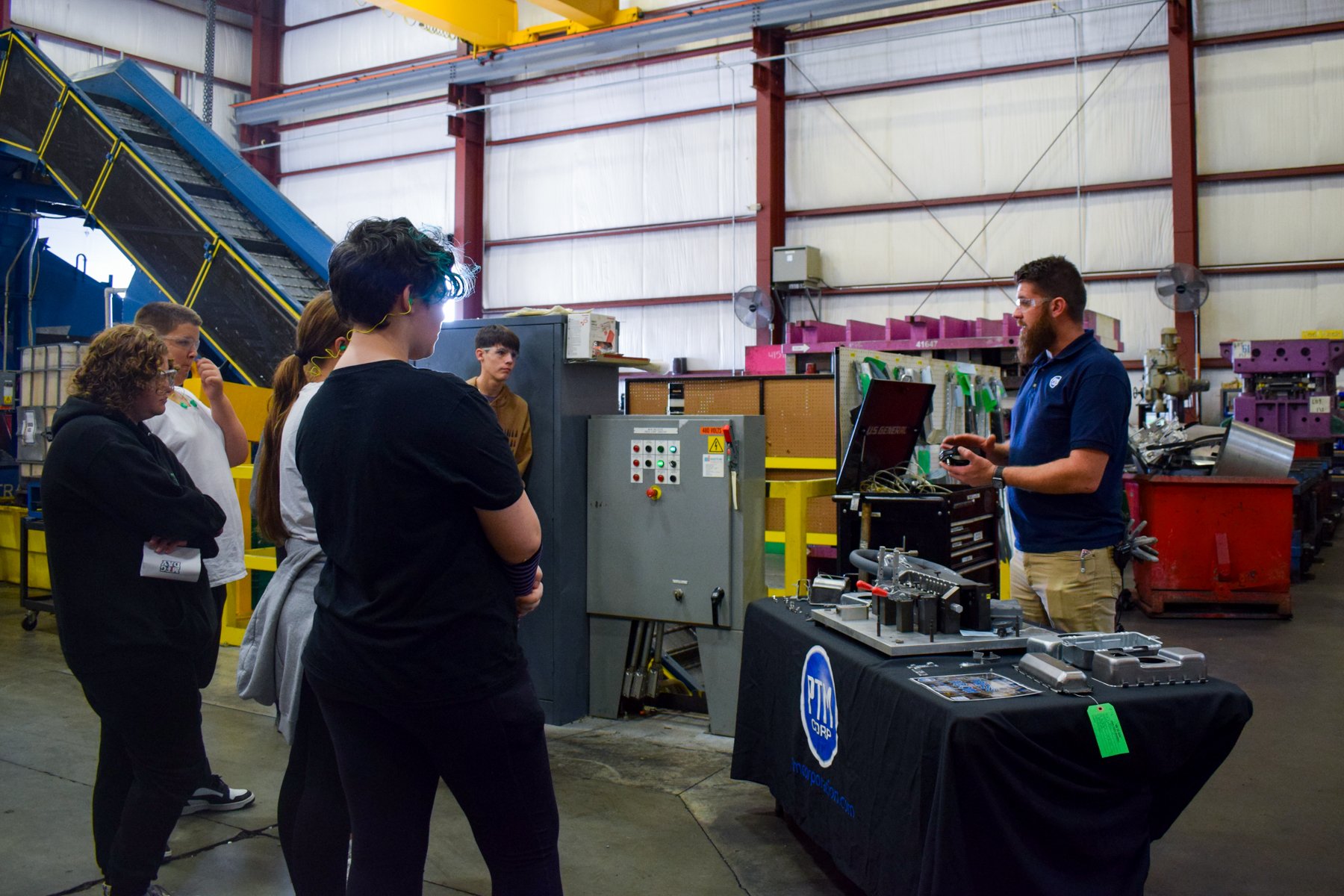
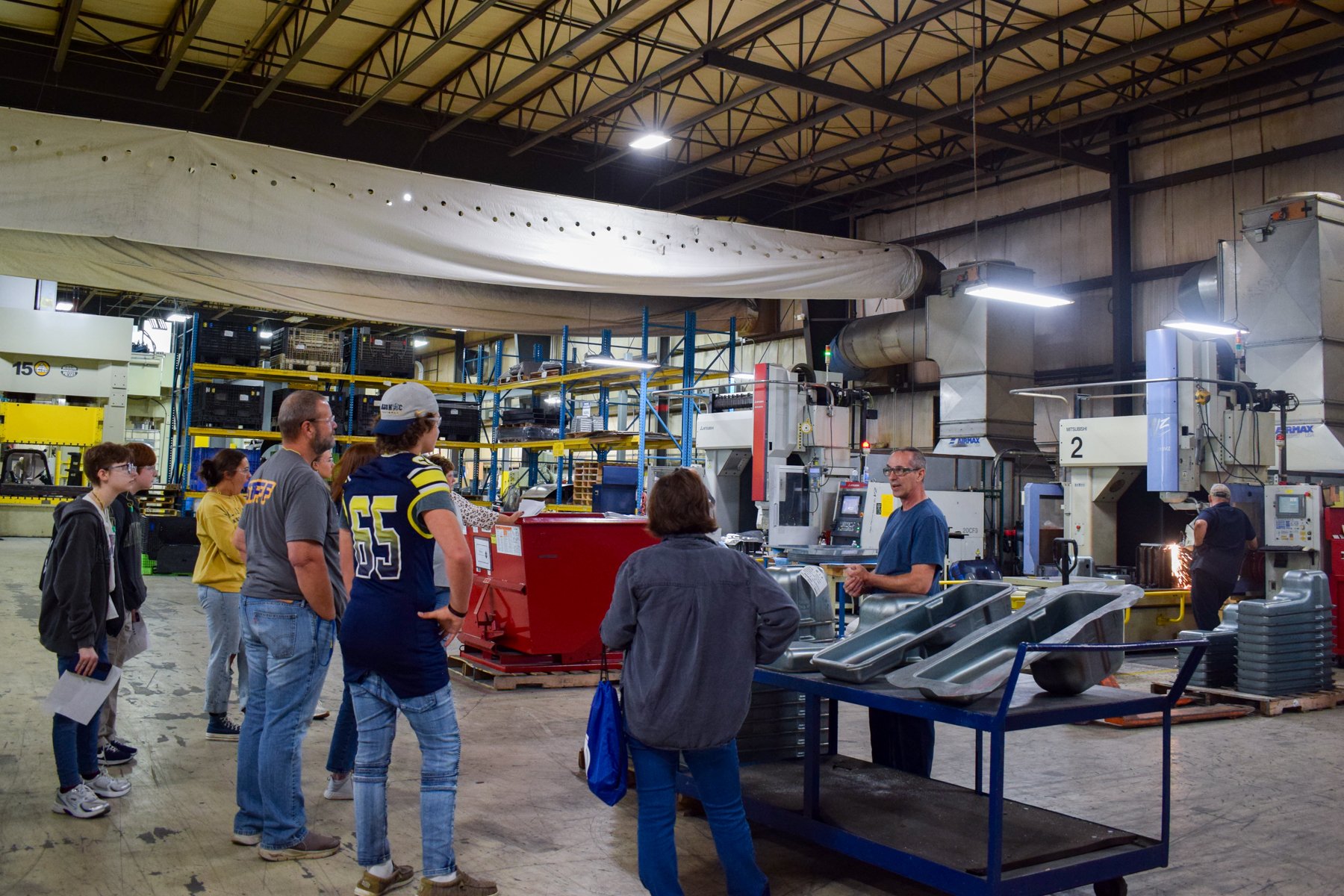































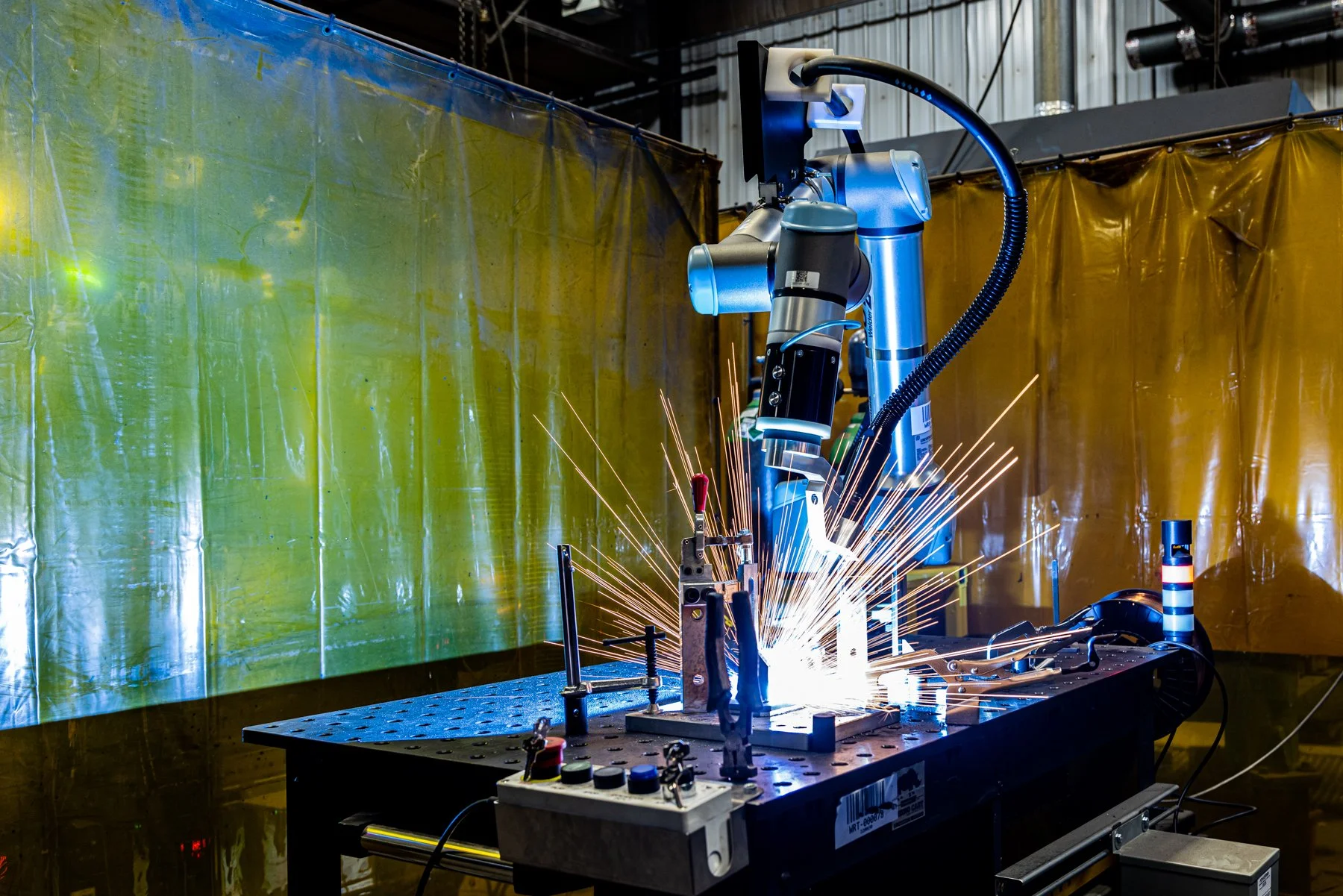
Station 1: COLLABORATIVE ROBOTS
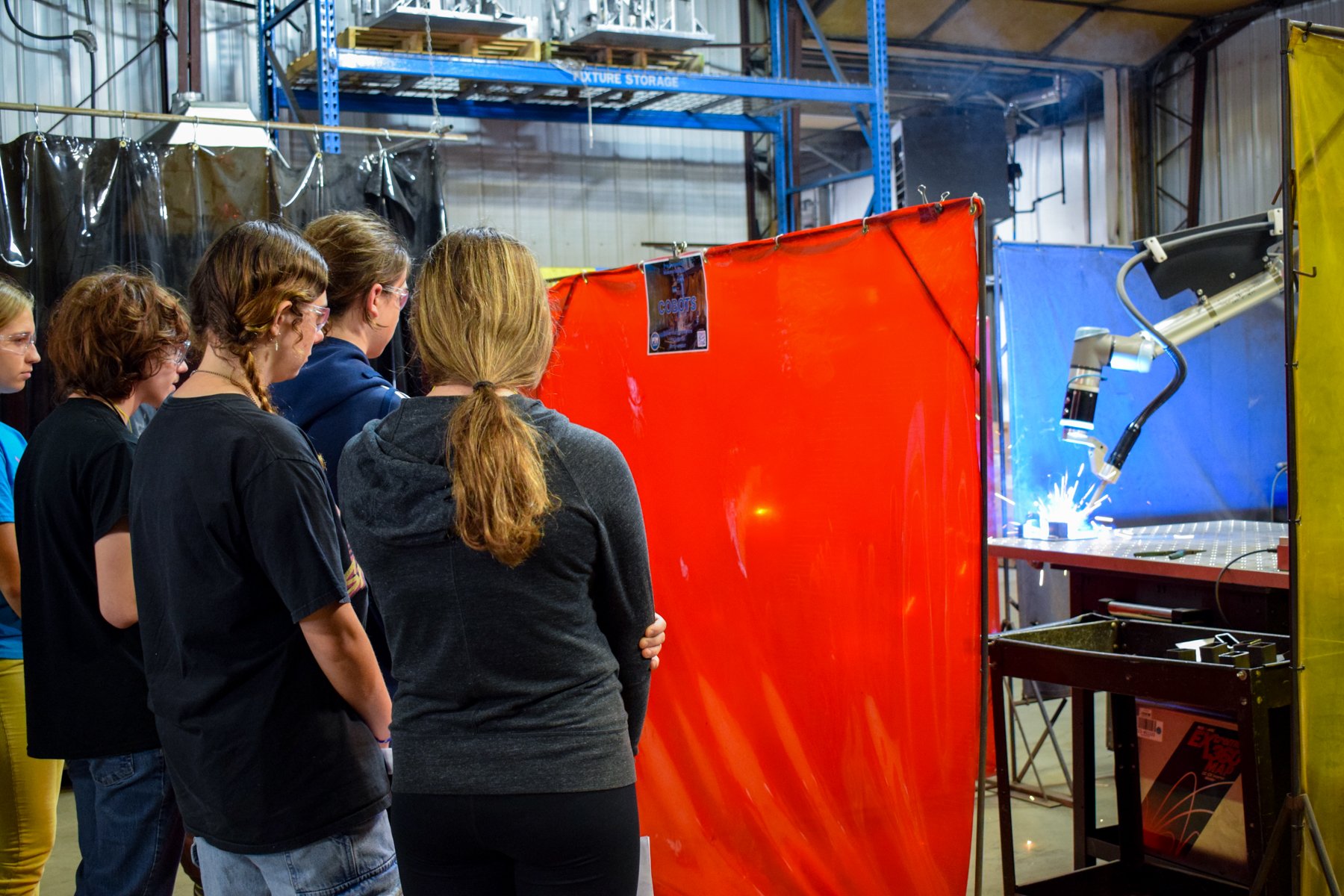
What are Collaborative Robots?
Cobots, or collaborative robots, are intended for direct human-robot interaction, where traditional robots are designed to operate in isolation. Cobots also differ in that they are very user friendly and require little training to write programs. Since they are designed to operate next to people, Cobots are designed with many safety features to ensure that no harm comes to the operator, or anyone in close proximity. Cobots are used in many applications such as welding, loading/unloading, sorting and inspection.
How are Cobot welders used in manufacturing?
Cobot welders are used to achieve greater precision, speed and consistency in parts requiring a welded construction.
Skillsets required?
A basic understanding of welding and programming.
Station 2: WIRE EDM
What is Wire EDM and what do they do?
Wire EDM is a machine used to cut individual die details that will form the part to be stamped out by the stamping die. EDM stands for electrical discharge machining. EDM Machines create an electrical discharge between a thin wire (or electrode) and the die being worked on. There is a gap between the wire and the die being worked on, an electric spark jumps across the gap causing material to be removed from both the die and the wire. A non conductive liquid prevents the process from shorting out and this liquid flushes out the removed material.
How is Wire EDM used in the manufacturing process at PTM?
Wire EDM is a machining process used to cut specific details on a die. Dies are created to stamp a specific parts. Dies are very expensive to make and they are not interchangable. For example you would not be able to use a die created to stamp a Jeep door to stamp a Chevy Cruze door. Dies are created to stamp a specific part. Modified Technologies Wire EDM machines use software to ensure the fastest, most accurate wire technology available. This means faster turn around time for our customers.
What type of products are made in the Wire EDM Department?
Large and small prototype parts are produced.
Skill Sets Required?
Language skills, math, and reasoning
Station 3: AEC BUILD
What is AEC Build?
Build Technicians weld parts to assemble products, using robotic welders, spot weld guns, or MIG and TIG welding. A basic assembly could have 40 to 50 parts and hundreds of welds. Build Technicians have an understanding of the heat required to weld the metal together, without burning through the part. The weight of the weld gun is counter balanced, which allows our technicians to precisely place their welds exactly in the required position.
Robotic weld cells are becoming common to our industry and are used to weld everything that you can imagine. These cells are designed to do full car bodies in white, before they are painted. Techs in this area are a combination of welder and computer programmer. They use Programmable Logic Controllers to map out the robots movements to perform each weld required to complete the assembly – which could number in the
Why is it helpful/important in manufacturing?
Within the process they Inspect assemblies and installation for conformance to specifications, using measuring instruments, such as calipers, scales, dial indicators, gauges, and micrometers.
What does AEC Build produce?
In this process they are welding assemblies in supportive framework according to blueprints and/or customer specifications.
Skill sets required?
Associates working in weld cells have a love for creating strong, neat precise welds. They possess a steady hand, a keen eye for detail and are proud of the parts they produce. Sometimes people go to school to get certified in welding, but more than likely they got their start learning from a family member or friend.
Station 4: NC MILLS
What is CNC Machining and what do they do?
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. CNC Machining is a process used in the manufacturing sector that involves the use of computers to control machine tools. Therefore a CNC Machine is automated, it is operated by precisely programmed commands stored on the machine.
How is CNC used in the manufacturing process at PTM?
• A CNC machine relies on digitial (number) instructions from a Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) or Computer Aided Design (CAD) file. Those computer instructions are used to transform a piece of material such as a block of plastic, metal or steel into a prototype or a die. Often a machining process needs multiple tools to make a desired cuts (different sized drill bits). CNC machines commonly combine tool into common units or cells from which the machine can draw.
• Basic machines move in 1 or 2 axes. Advanced machines can move laterally in the x, y axis, longitudinally in the z axis, and oftentimes rotationally about one or more axes. This allows the machine to flip a part over and remove material underneath it. This is good because it eliminates the need for a worker to flip the prototype stock material. Using a computer to cut parts provides a more accurate cut than manual cuts made by a person. This allows that person time to complete finishing work like etching, or simple cuts which is better when it is done by hand because the extensive design and programming for the machine automation.
• CNC technology is highly specialized and is used in special cases for mass-production involving a particular type.
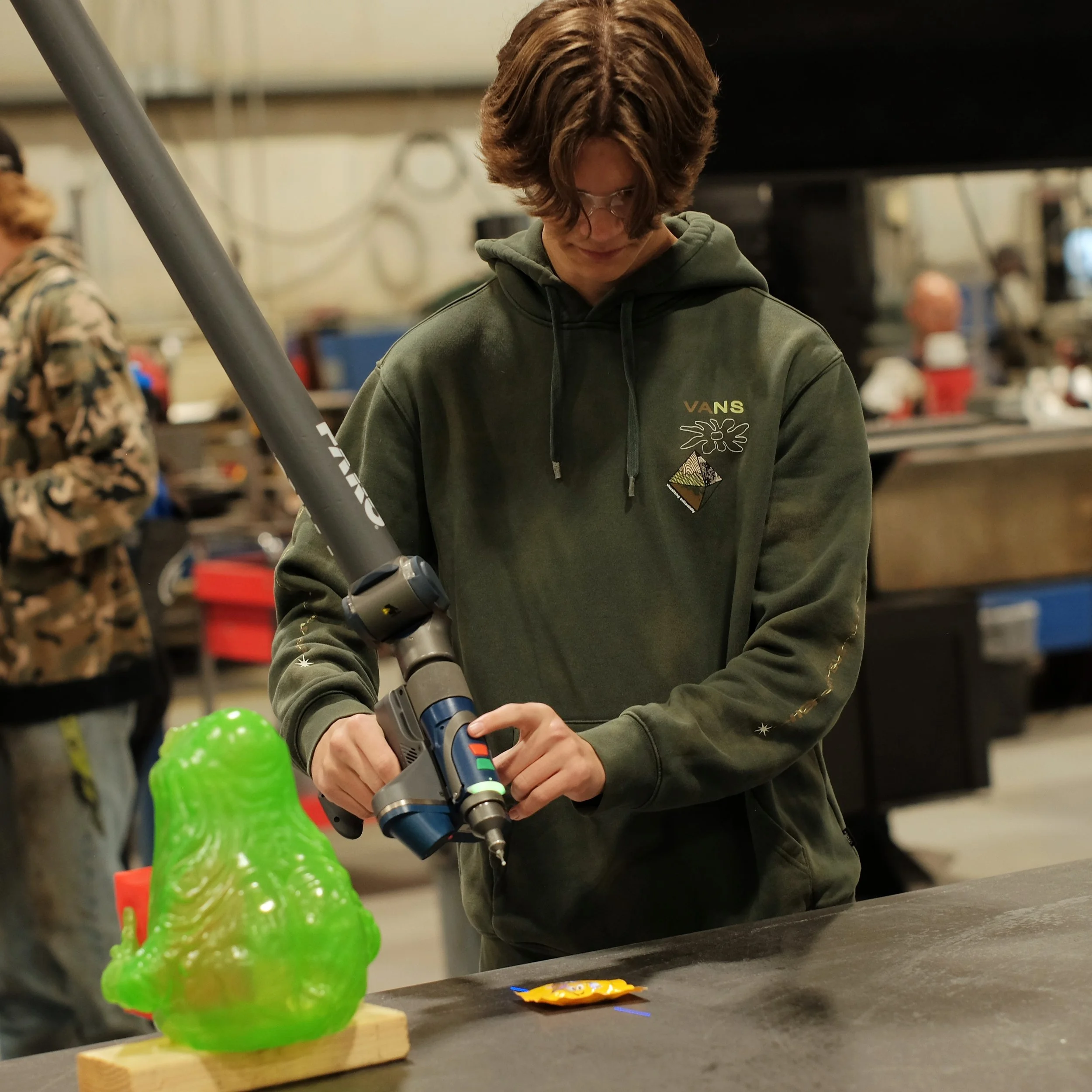
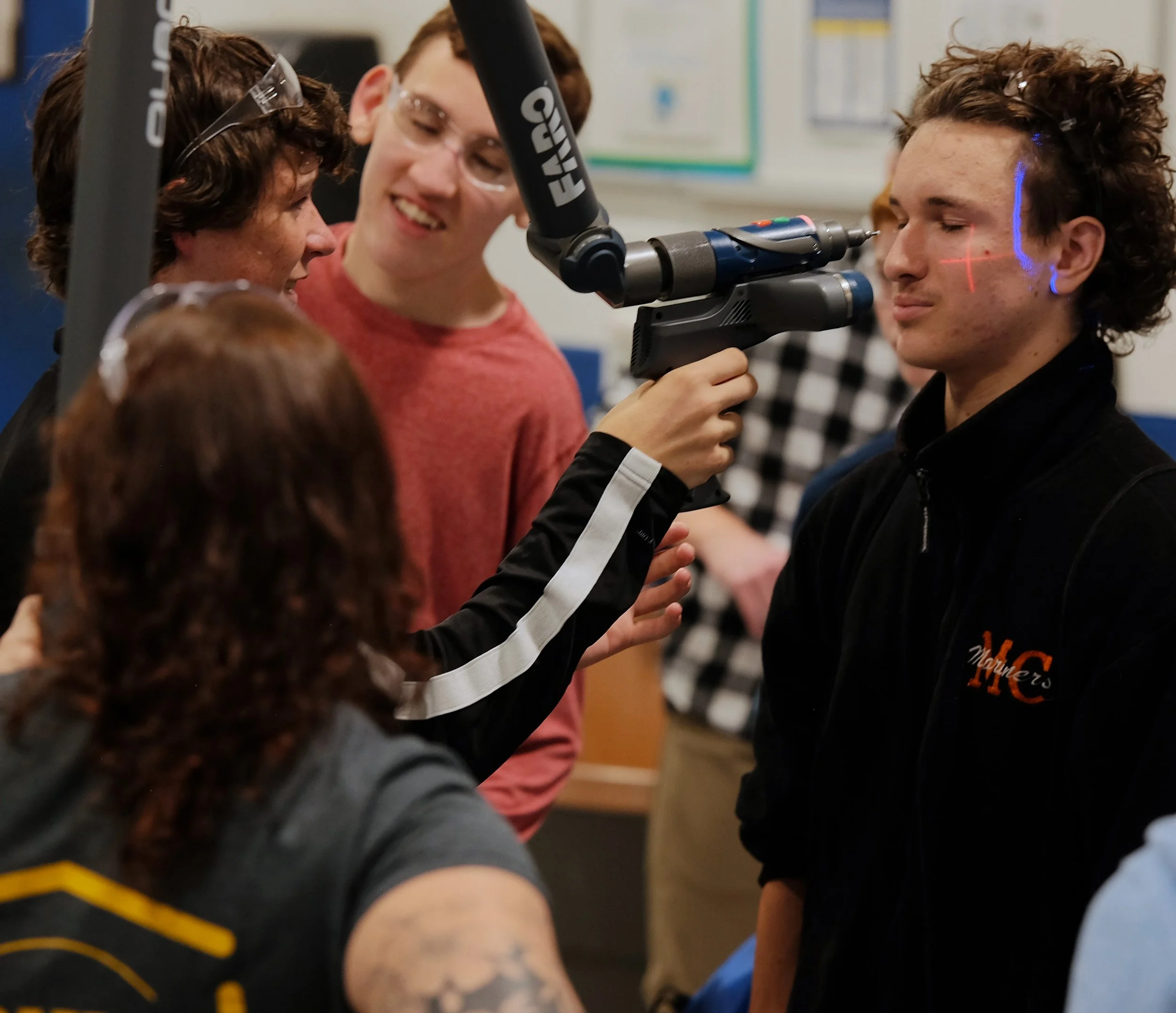
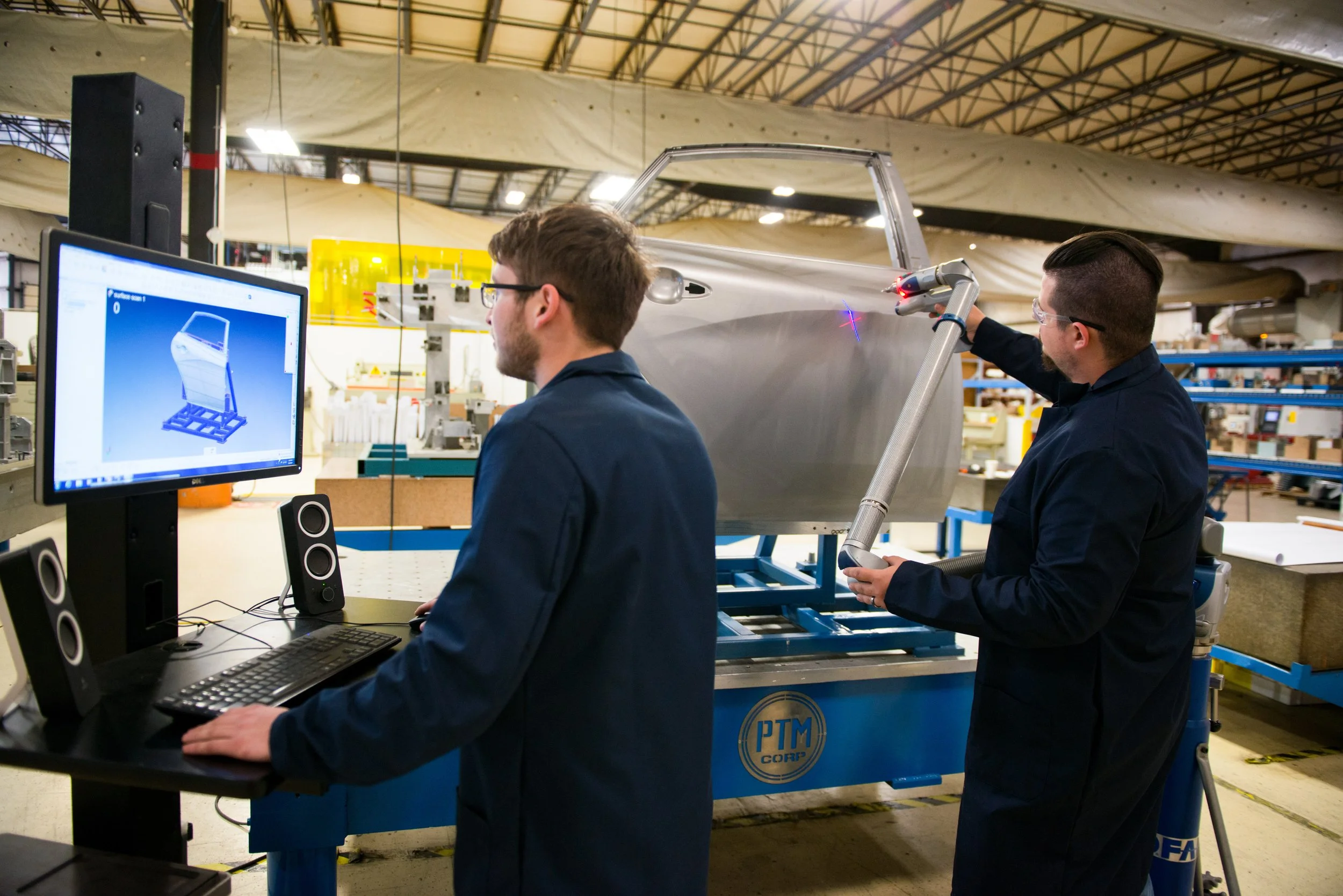
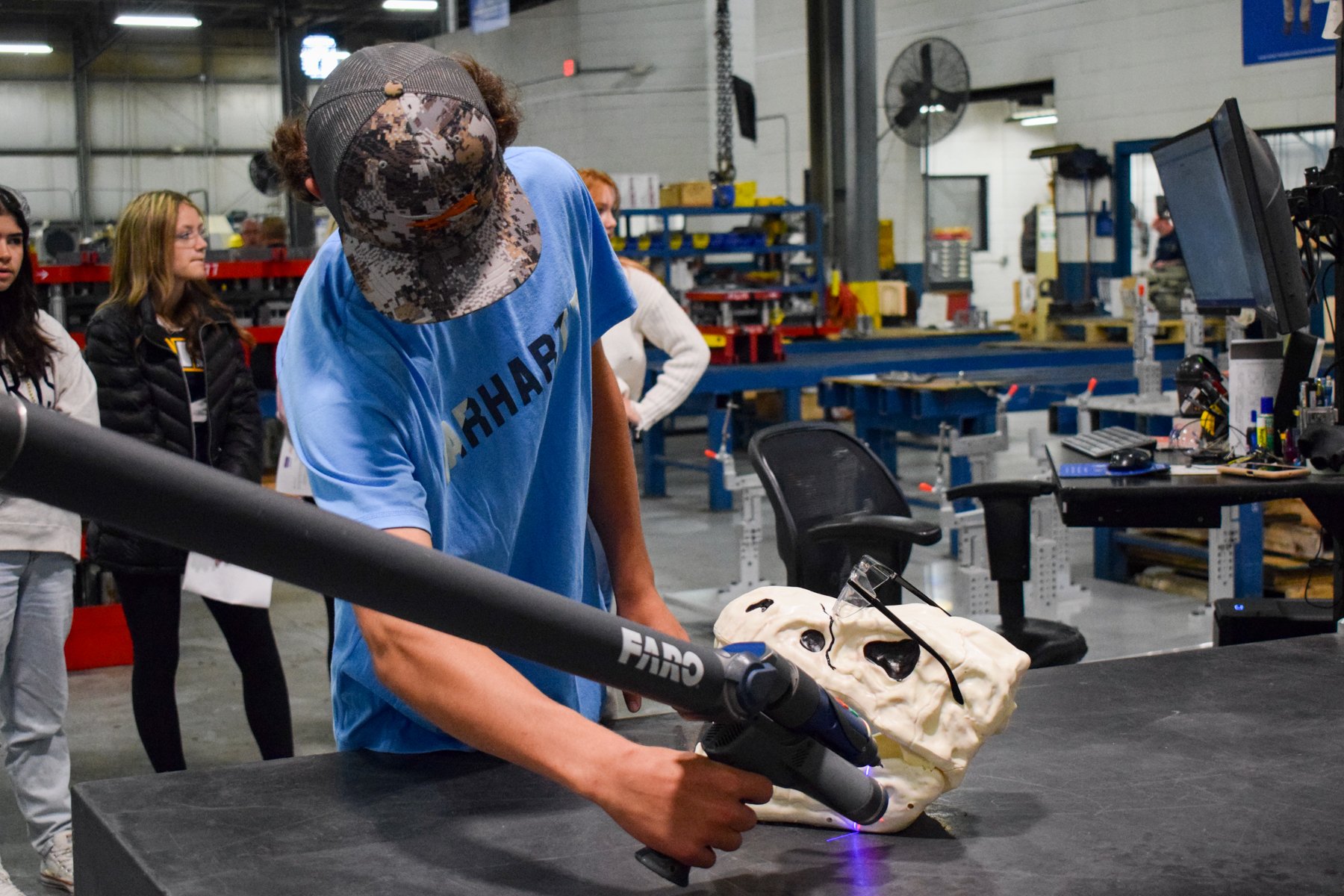
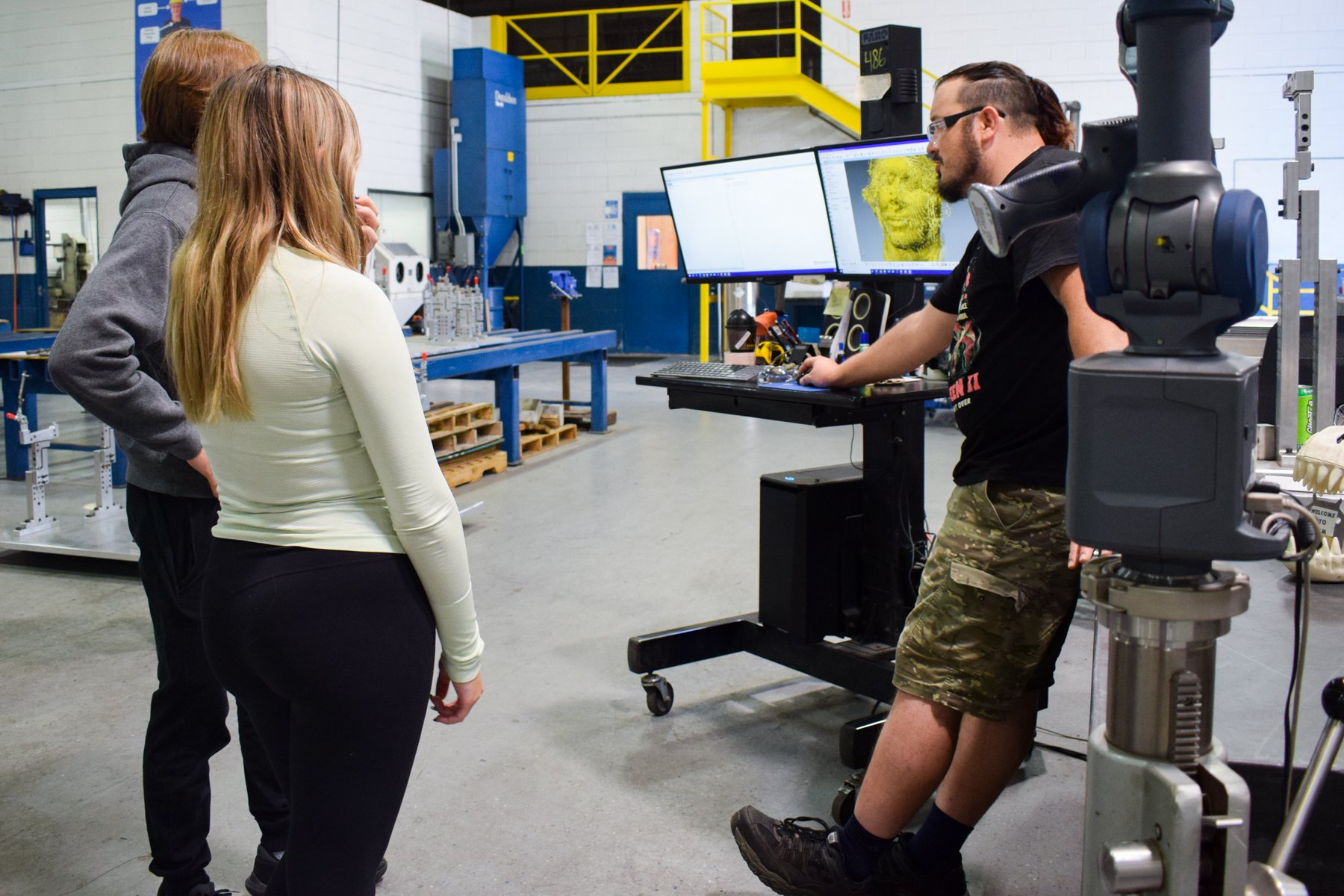
Station 5: FARO ARM
The FARO arm uses the high tech ability of a blue light laser, to scan & measure parts and fixtures providing 1.2 million measurement points per second (PAR) with an accuracy rate of 1-1000 of an inch.
This process provides a quick and accurate way of measuring and providing quick data back to the manufacturing floor for improvements on products and also provides the customer with accurate data in the form of an inspection report with full color mapping of parts or assemblies manufactured.
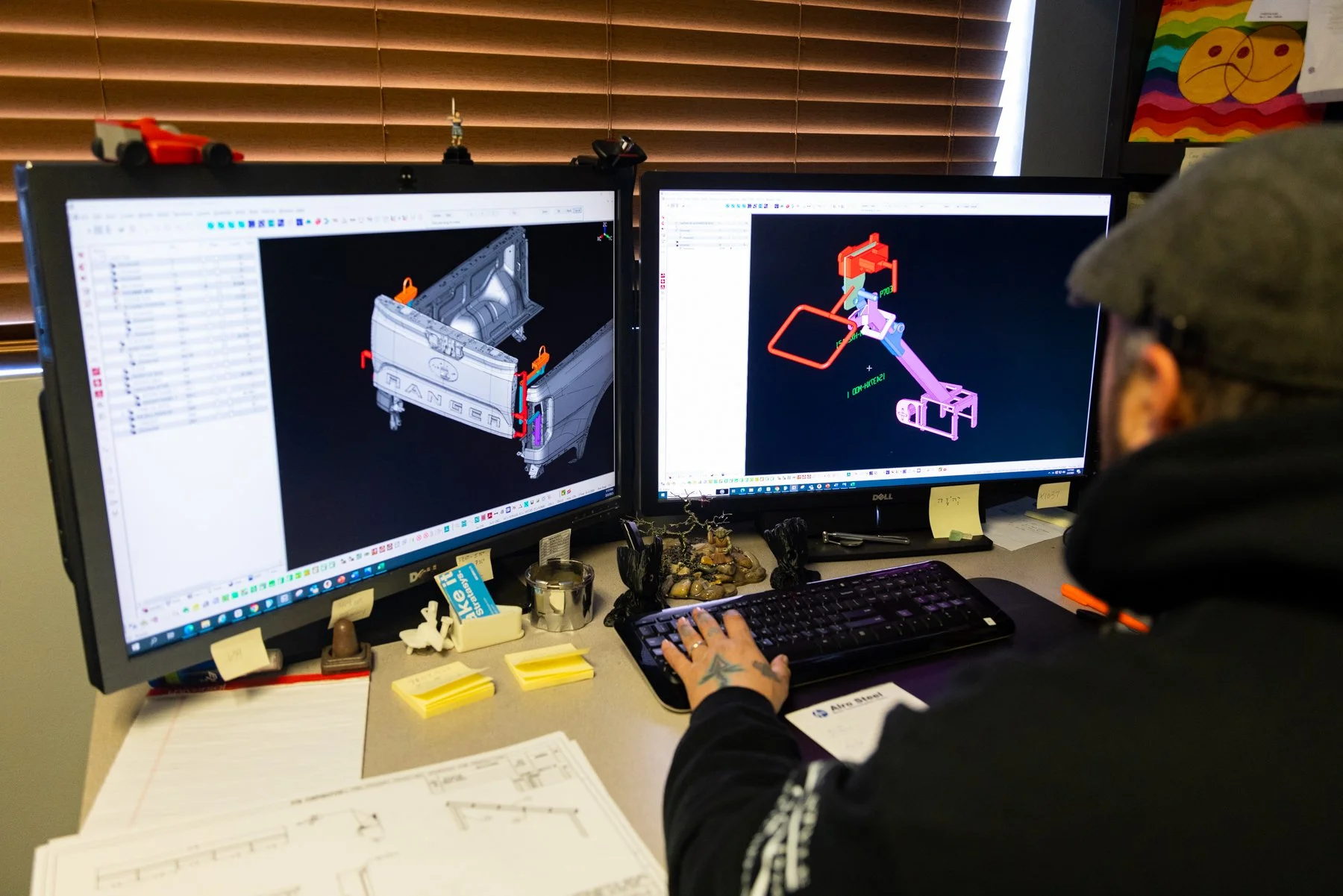
Station 6: DESIGN
What is Design and what do they do?
PTM Corporation has a product designers, paint tool design and build designers, and CAD systems designers. Designing a tool, or a prototype for a customer may start as something very simple, like an idea sketched on a napkin, a drawing or sometimes its just a written description of what the customer needs. Although design may seem a bit "artsy" the truth is Design is a systematic approach that considers the customers need, the application for their product, the type of material(s) needed for the build and for the finished product, and it may consider the number of pieces needed among many other key factors.
How is Design used in the manufacturing process at PTM?
Once a design is completed, we make our design recommendations for both the product and tooling to manufacture it. Whether the designer is working on a product design, working on paint tool designs and builds, or designing in a CAD (Computer Aided Design) system, the goal at PTM is to maximize the ROI (Return on Investment) of our customers spend dollars both in the design phase and in the part production phase.
What type of products are made in the Design Department?
Whether the customers design is on a napkin, or still in their head, the benefits of having PTM Designers involved early in the customer product design include:
Lower cost, quick turnaround from concept to completion, minimize material requirements and manufacturability, improved quality and functionality, minimize tgooling costs, prototyping, and we have a cross functional campus relationship with PTM tooling and PTM production.
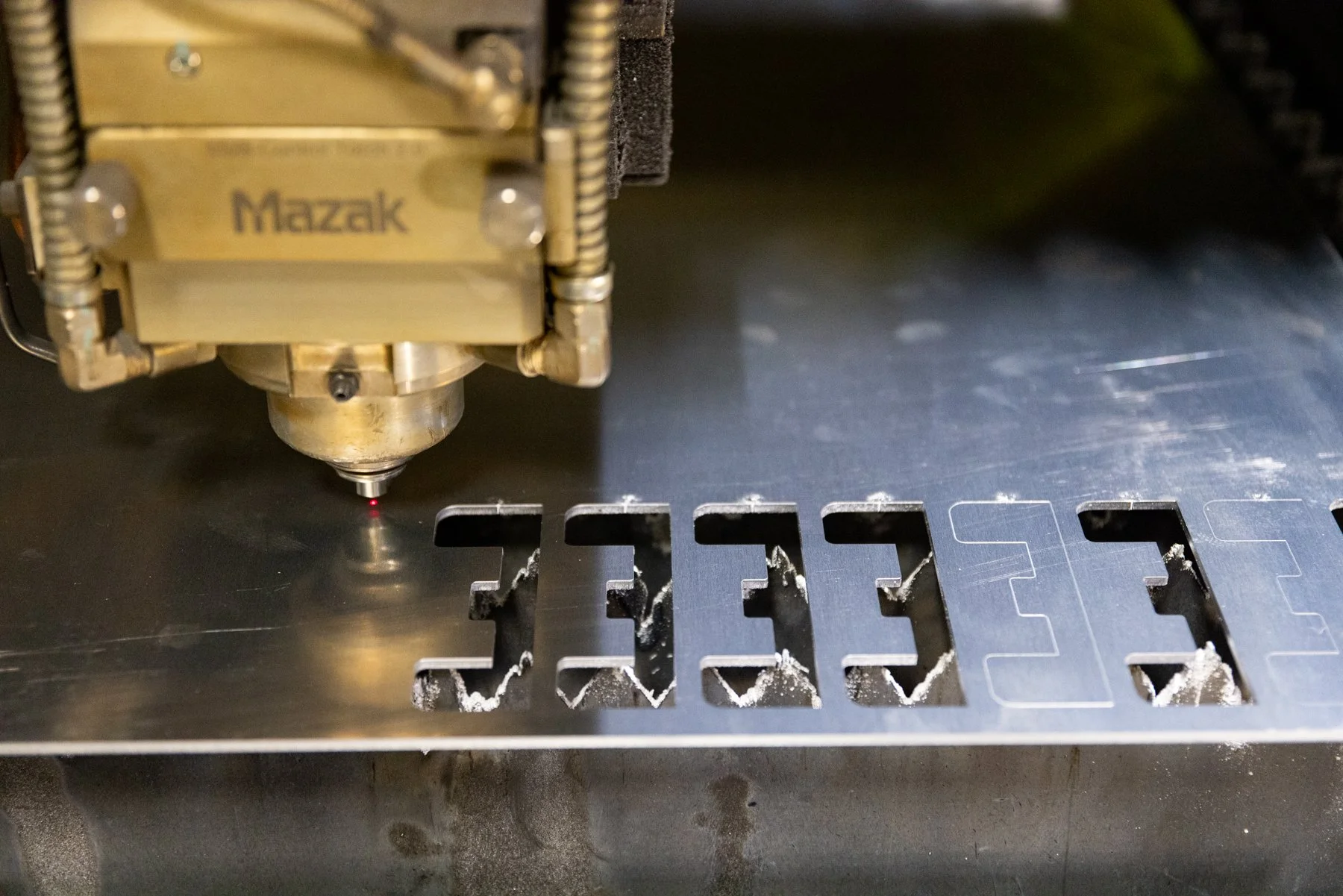
Station 7: LASER
What is Laser?
Lasers are used for a wide range of manufacturing applications. They can be used for precision cutting, drilling, micromachining, and engraving.
Why is laser used in manufacturing?
• Here at PTM we use a 5 Axis Laser for cutting and prototyping to meet our design and customer specifications. The 5 axis laser is used to trim excess metal off a rapid prototype part.
Three-dimensional laser cutting systems offer the ultimate in accuracy and flexibility for users across a wide range of complex cutting applications. The unique flexibility of these 5 axis systems make them extremely powerful tools. They significantly decrease the time and manpower required to produce complex parts, and provide the greatest degree of accuracy and cost efficiency.
What does it produce?
• Our lasers are cutting carbon, alloy, stainless steel and aluminum to name a few. Lasers are used to enhance parts and/or meet a prototype specification. For example a laser might take a part that has already been made and then use a laser to make a bend in that part or to change the form of the part. We might want to countersink a particular area of a part. Lasers can be used for tapping on a part, milling and welding.
5 Axis Laser can: (Refer to parts display)
3D cuts in almost all planes (x, y, z)
Cut any geometry in any location
Cut stainless steel, aluminum, steel, and galvanized steel
Bevel holes
Skill Sets Required?
Associates operating this equipment need to understanding of PLC – Programmable Logic Controllers and how to make the laser’s cutting head move to perform the required cutting operations.
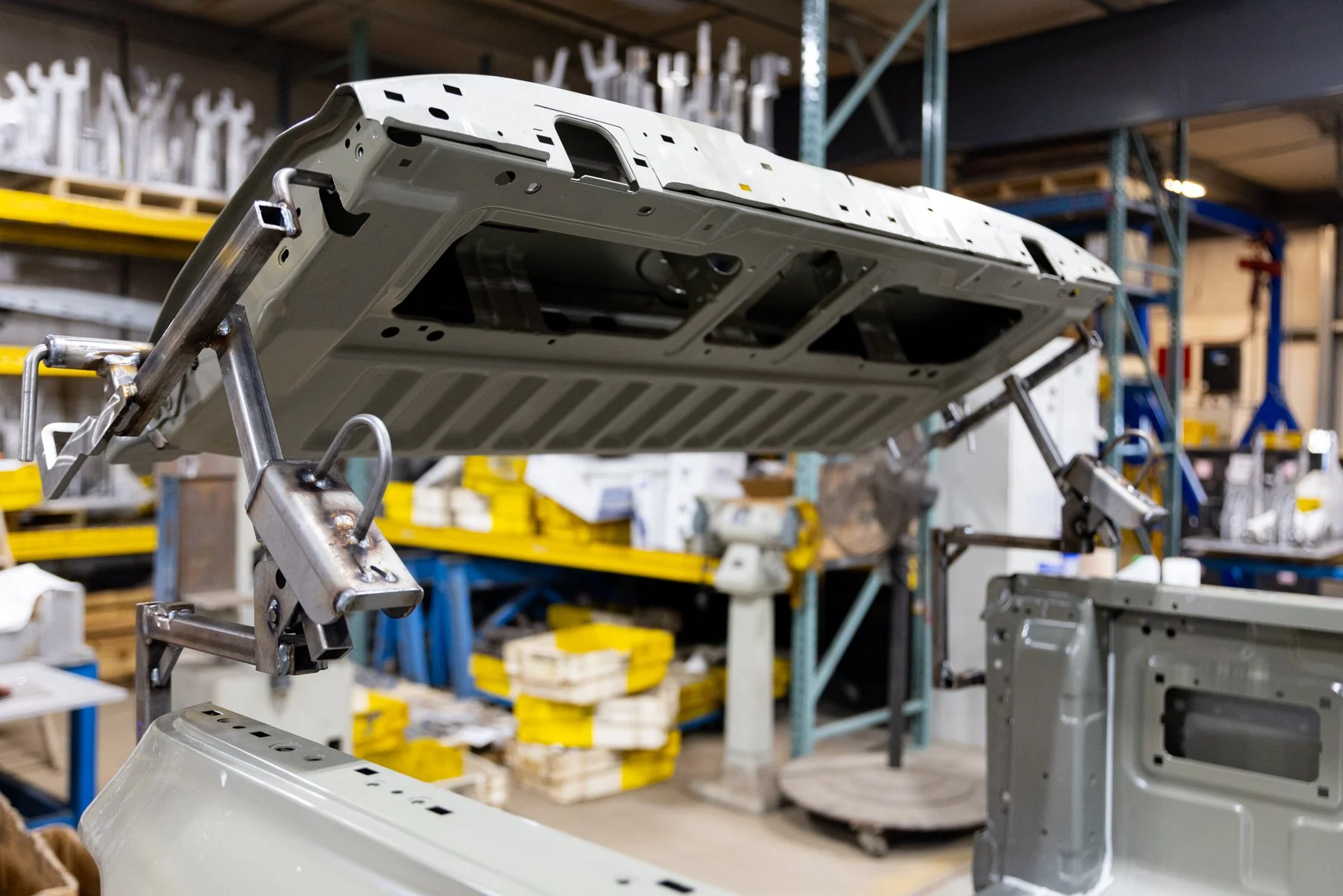
Station 8: PROTOTYPE
What is Prototype?
A first or preliminary working model of something that will be developed and patterned from. We take ideas and turn them into reality.
Why do we need to Prototype parts?
Prototype is used to prove out a design concept by testing function and manufacturing feasibility. We can build 1 piece or 1,000 pieces depending on the customer needs.
What do we make it Prototype?
We make clips, brackets and weld assemblies that help automotive companies manufacture their vehicles. To make the products we use Mechanical and Hydraulic Presses, Brake Presses, Laser Machines, Mills, Lathes, MIG and TIG Welders, Resistance Welders and hands on fabrication. We also run low volume production which can be as high as 100,000 pieces or more.
Skill Set Required?
CAD, Math, Manual Machining, Tool Making, Tool Set Up, Tool Tryout, Quality Measurement, Problem Solving
Station 9: ASSEMBLY
What is Assembly?
You may not have noticed but almost everything you buy has more than 1 part. Take an ink pen for example. It has several parts and a "moving" part. Assembly in the manufacturing process consists of putting together, or "assembling" all of the components, parts and sub-assemblies of a given product. Some methods used in manufacturing assembly include machining, grinding, and welding. Most of these operations are completed more accurately and efficiently with the aid of equipment. Accuracy and efficiency saves time and money. The development of automated methods has been necessary rather than optional in order to compete in business. Assembly on the other hand may involve one machine. Many of the fastening methods such as riviting, welding, screwdriving and adhesive applications.
Why is it helpful/important in manufacturing?
Manufacturing is critically important to the American economy. For generations the strength of our country rested on the power of our factory floors. Both the machines and the men and women who worked them. Manufacturing assemblies account for 12 percent of the US economy and about 11% of private-sector workforce.
What does assembly produce?
At PTM Corporation we produce quality parts to our customers with 100% on time delivery. Assembly includes fastening, performing inspections and functional tests, labeling, separating good assemblies from bad, and packaging and preparing parts for final use.
Skill sets required?
Ability to multi-task
Good problem solving skills
Willingness to learn
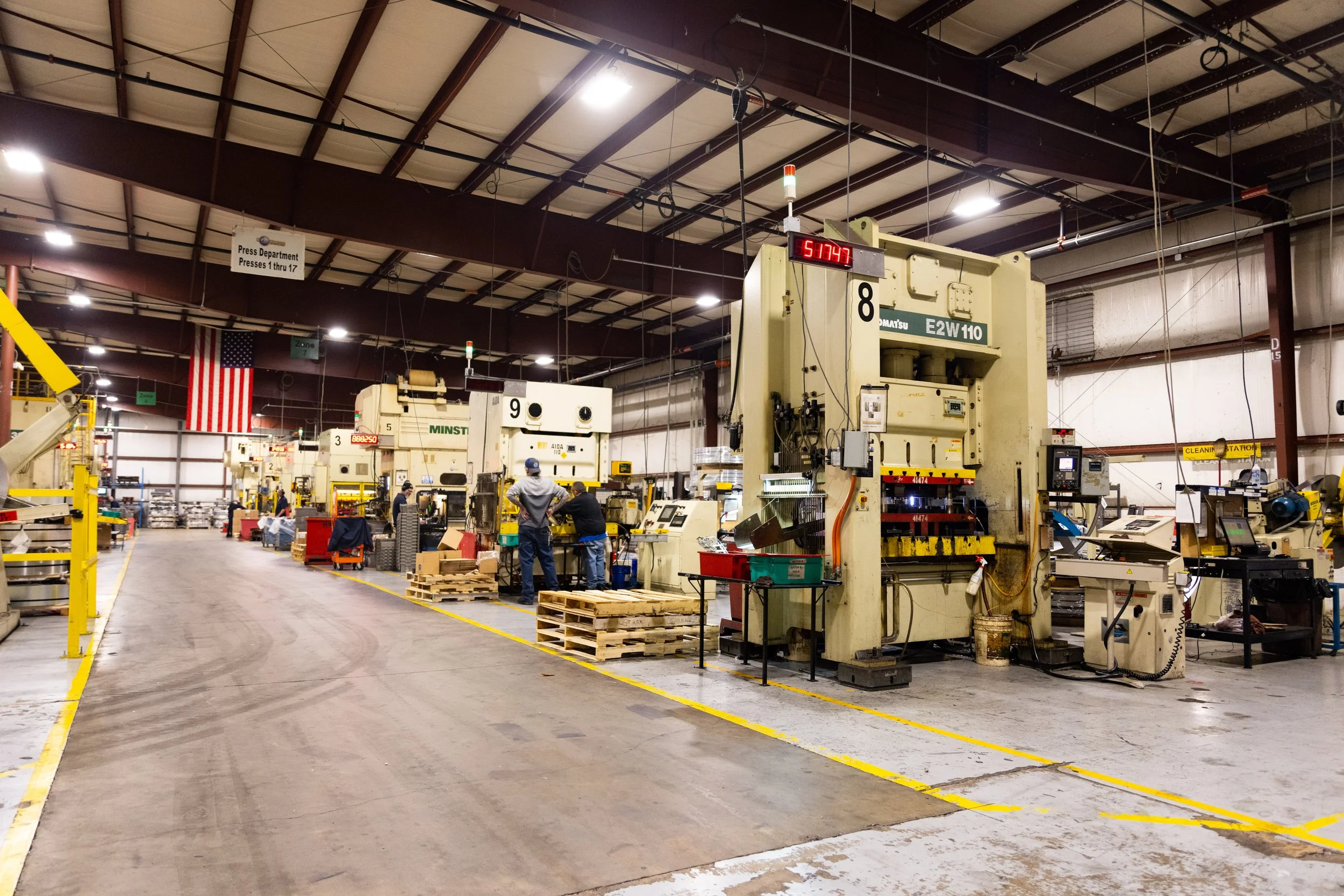
Station 10: PRESSROOM
What is Stamping?
Progressive stamping is a metalworking method that can encompass punching, coining, bending and several other ways of modifying metal raw material, combined with an automatic feeding system.
The feeding system pushes a strip of metal (as it unrolls from a coil) through all of the stations of a progressive stamping die. Each station performs one or more operations until a finished part is made. The final station is a cutoff operation, which separates the finished part from the carrying web. The carrying web, along with metal that is punched away in previous operations, is treated as scrap metal.
Both are cut away, knocked down (or out of the dies) and then ejected from the die set, and in mass production are often transferred to scrap bins via material conveyor belts.
The progressive stamping die is placed into a reciprocating stamping press. As the press moves up, the top die moves with it, which allows the material to feed. When the press moves down, the die closes and performs the stamping operation. With each stroke of the press, a completed part is removed from the die.
Since additional work is done in each "station" of the die, it is important that the strip be advanced very precisely so that it aligns within a few thousandths of an inch as it moves from station to station. Bullet shaped or conical "pilots" enter previously pierced round holes in the strip to assure this alignment since the feeding mechanism usually cannot provide the necessary precision in feed length.
The dies are usually made of tool steel to withstand the high shock loading involved, retain the necessary sharp cutting edge, and resist the abrasive forces involved, but things do happen. We have an entire department dedicated to keeping these tools working as they should.
Why is stamping used in manufacturing?
Stamping is used in just about every manufacturing industry to make parts to specific specifications. We currently have presses working at 120 strokes per minute, which means that they are producing 120 parts per minute. As you can see parts can be very intricate and complex (reference the parts display).
What does it produce?
At PTM we produce a wide range of products used in various industries such as the automotive industry, the military, agriculture, and appliance, etc. These parts are designed, stamping machines are calibrated to the design specifications and then the parts are made by a stamping maching. Some of those products include:
Wrap brackets
Air bag components
Complex, high precision fuel line connectors
Tight tolerance fasteners
Brackets
Roof components
Conveyor components
Clips
Terminals
Heat shields
Bushings
Many others
Skill Sets Required?
Each of our Press Room associates started as press operators but eventually became die setters at some time during their career. They know how to position the die in the press in order to produce the part to the customer’s specification. Die Setters are highly skilled and good ones are in great demand by manufacturers.